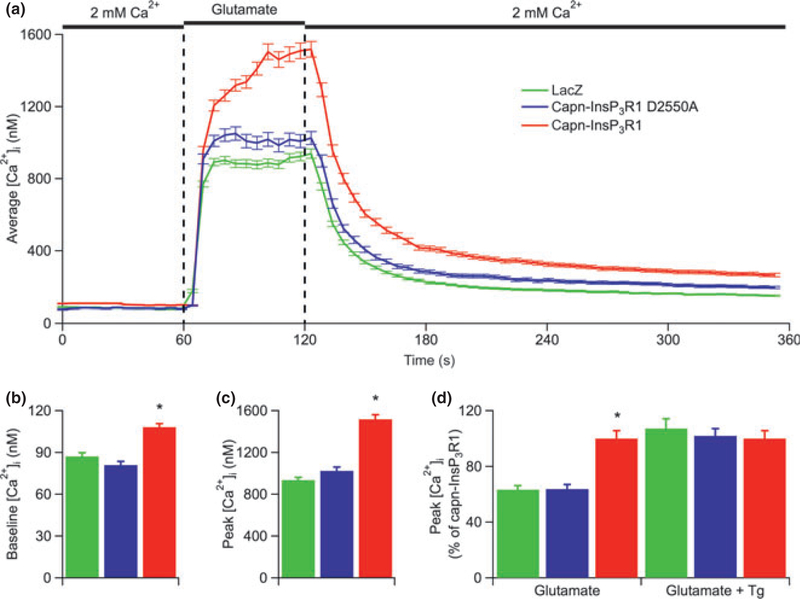
Fig. 4.
Neurons expressing capn-InsP3R1 have increased glutamate-induced rises in [Ca2+]i. (a) Averaged single-cell [Ca2+]i responses to glutamate in Fura-2-loaded primary cortical neurons (14 DIV) transduced with lacZ, capn-InsP3R1 D2550A, or capn-InsP3R1. Total number of single-cell Ca2+ responses analyzed in these experiments was 491, 271, and 396 for lacZ-, capn-InsP3R1 D2550A-, and capn-InsP3R1-transduced cultures, respectively. (b) Summary of average resting [Ca2+]i in neurons from cultures used for glutamate Ca2+ imaging experiments. Expression of capn-InsP3R1 significantly increased resting [Ca2+]i in neurons (108.2 ± 2.6 nM) compared with capn-InsP3R1 D2550A (81.0 ± 2.5 nM) and lacZ controls(87.3 ± 2.6 nM; unpaired t-tests with unequal variance; *p < 0.001).(c) Summary of average peak [Ca2+]i responses elicited by glutamate shows an increased maximum [Ca2+]i achieved in capn-InsP3R1-expressing cells (unpaired t-tests with unequal variance; *p < 0.001).(d) Summary of average peak [Ca2+]i elicited by glutamate in the absence or presence of Tg (normalized data for glutamate alone (left) are the same as absolute data shown Fig. 4c). Total number of single-cell Ca2+ responses analyzed in experiments with Tg was 182, 209, and 146 for lacZ-, capn-InsP3R1 D2550A-, and capn-InsP3R1-transduced cultures, respectively. Tg eliminated the capn-InsP3R1-associated glutamate-induced enhanced peak [Ca2+]i (lacZ, 1,357 ± 66 nM; capn-InsP3R1 D2550a, 1,276 ± 44 nM; capn-InsP3R1, 1,288 ± 54 nM).