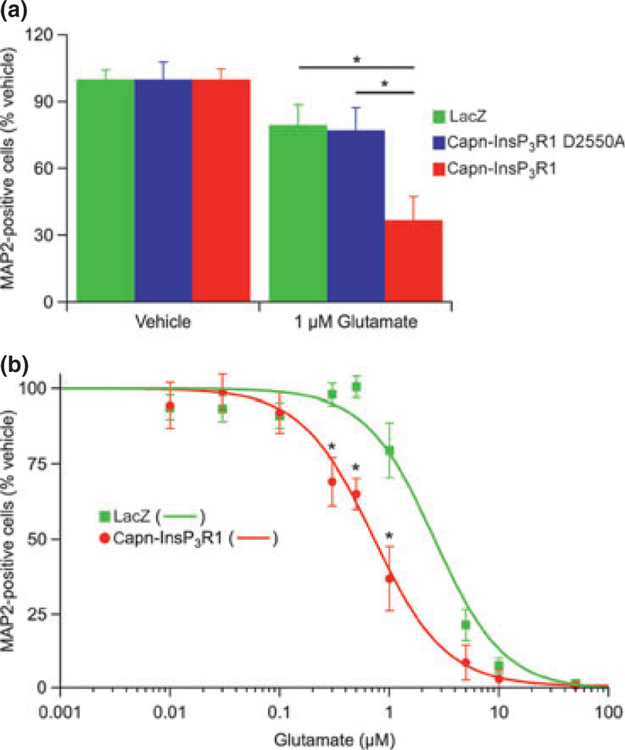
Fig. 5.
Expression of capn-InsP3R1 increases neuronal susceptibility to glutamate-mediated injury. (a) Transduced primary cortical cultures (14 DIV) were exposed to 1 μM glutamate or HEPES-buffered saline vehicle. Twenty-four hours later, cultures were stained for microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) and percent neuronal survival quantified relative to vehicle-treated cultures. Expression of capn-InsP3R1 resulted in a significant decrease in percentage of MAP2-positive cells following glutamate injury compared with lacZ and capn-InsP3R1 D2550A (one-way ANOVA; *p < 0.01). (b) Glutamate dose-response curves for lacZ and capn-InsP3R1-transduced cultures (data at 1 μM glutamate are the same as shown in Fig. 5a). Expression of capn-InsP3R1 significantly decreased percent MAP2-positive cells following treatment with 0.3, 0.5, and 1 lM glutamate compared with lacZ (unpaired t tests; *p < 0.01) and resulted in a shift in the glutamate dose-response curve. LD50 for glutamate in neurons expressing capn-InsP3R1 (0.75 ± 0.19 μM) is reduced compared with neurons expressing lacZ (2.61 ± 0.78 μM).