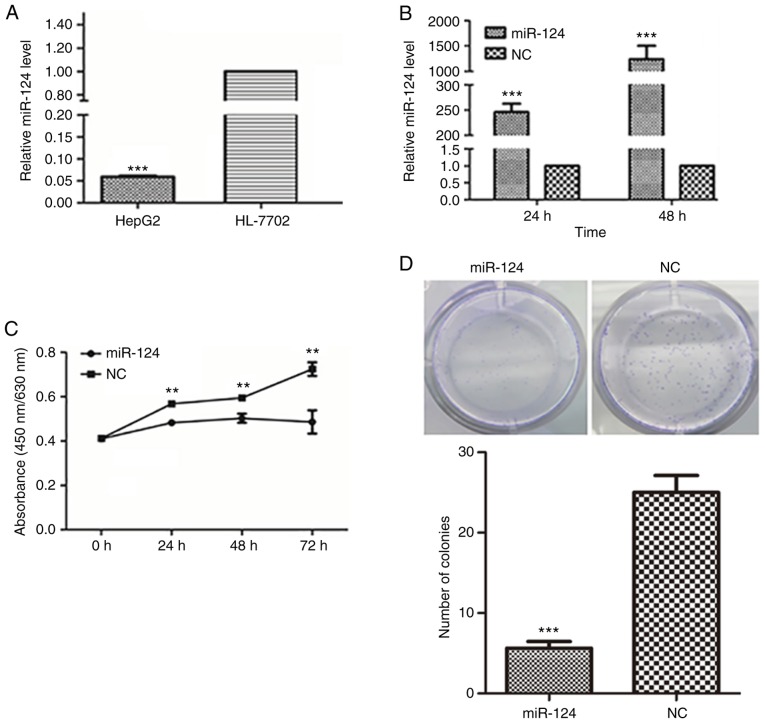
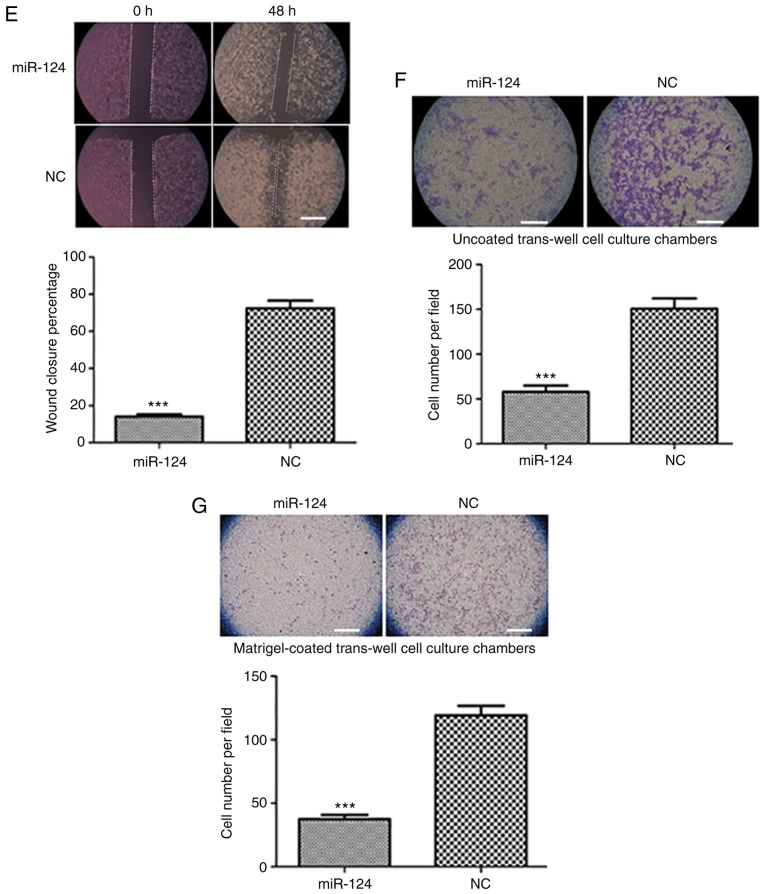
Figure 1.
Ectopic expression of miR-124 suppresses liver cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. (A) Detection of the miR-124 expression level in human liver cancer cells and a normal liver epithelial cell line by RT-qPCR with normalization to U6 ***P<0.001 vs. HL-7702. (B) Evaluation of the efficiency of the miR-124 precursor at 24 and 48 h after transfection using RT-qPCR. (C) Summary of the effect of miR-124 on the viability of liver cancer cells, according to the water soluble tetrazolium salt-1 assay. (D) Colony formation assay showing the effect of miR-124 on the cell growth of liver cancer cells. Scale bar, 200 µm. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. respective NC. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; miR, microRNA; NC, negative control. (E) Analysis of the function of miR-124 on the migration of liver cancer cells by scratch wound-healing motility assay. Scale bar, 200 µm. (F) The effect of miR-124 on the migration of liver cancer cells in the Transwell assay without Matrigel coating. Scale bar, 200 µm. (G) A Matrigel-coated Transwell assay was used to analyze the effect of miR-124 on cell invasion in liver cancer cells. Scale bar, 200 µm. ***P<0.001 vs. respective NC. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; miR, microRNA; NC, negative control.