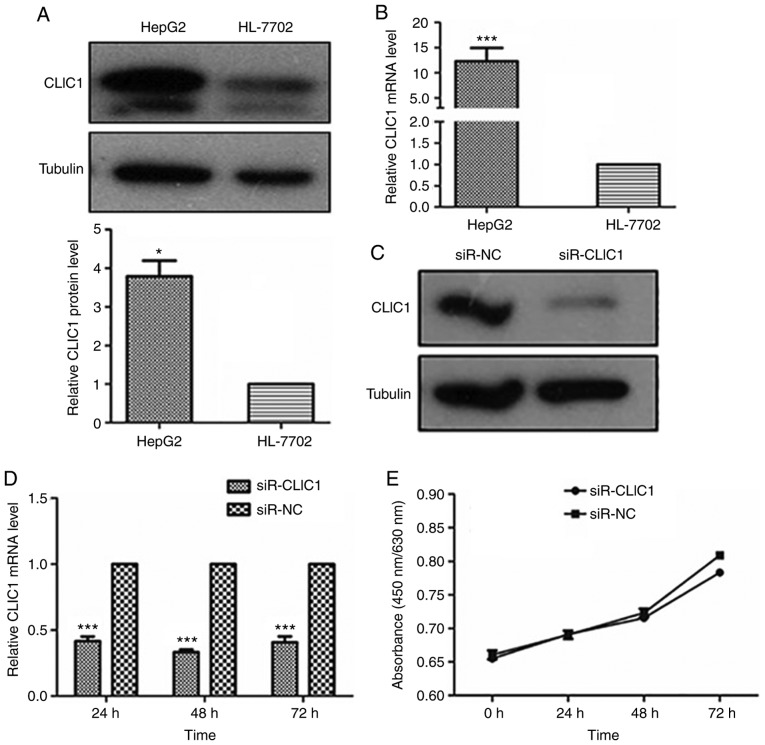
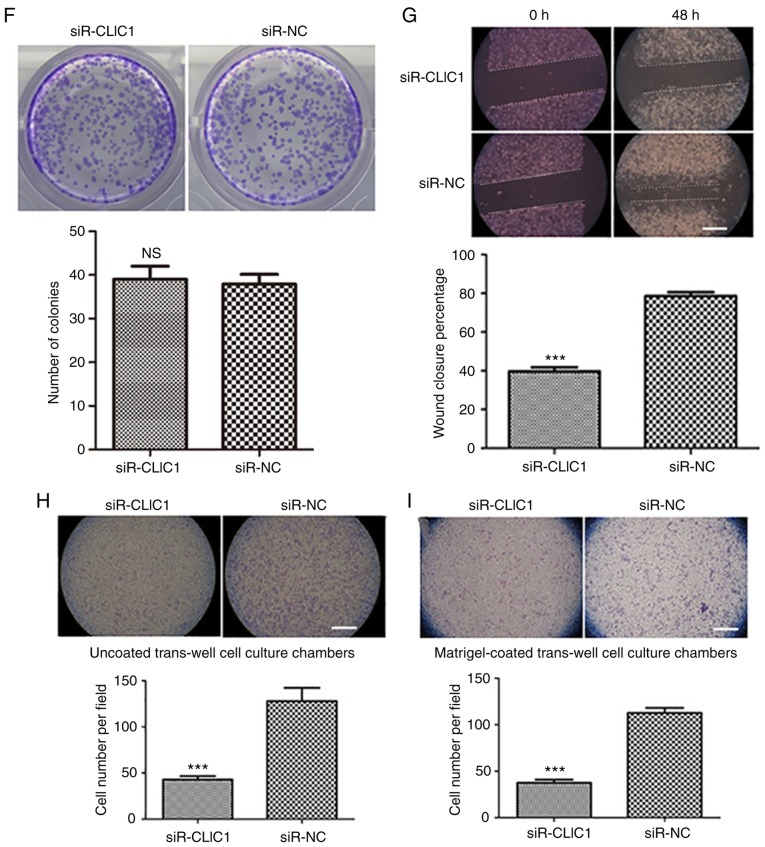
Figure 3.
CLIC1 is essential for liver cancer cell migration and invasion, but not proliferation. (A) CLIC1 protein is overexpressed in liver cancer cells compared with normal liver epithelial cells. (B) Analysis of the mRNA expression level of CLIC1 by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs. HL-7702. (C) CLIC1 protein and (D) mRNA were reduced by siR-CLIC1 in liver cancer cells. (E) WST1 showed that CLIC1 had no effect on cell viability and cell growth. siR, small interfering RNA; CLIC1, chloride intracellular protein 1; NC, negative control; n.s., not significant. (F) Colony formation assays showed that CLIC1 had no effect on cell viability and cell growth. The cell migration of liver cancer cells after knockdown of CLIC1 was evaluated by (G) scratch wound-healing motility assay and (H) Transwell assay without Matrigel coating. Scale bar, 200 µm. (I) The cell invasion ability of liver cancer cells was evaluated by Matrigel-coated Transwell assay. Scale bar, 200 µm. ***P<0.001 vs. respective siR-NC. siR, small interfering RNA; CLIC1, chloride intracellular protein 1; NC, negative control; n.s., not significant.