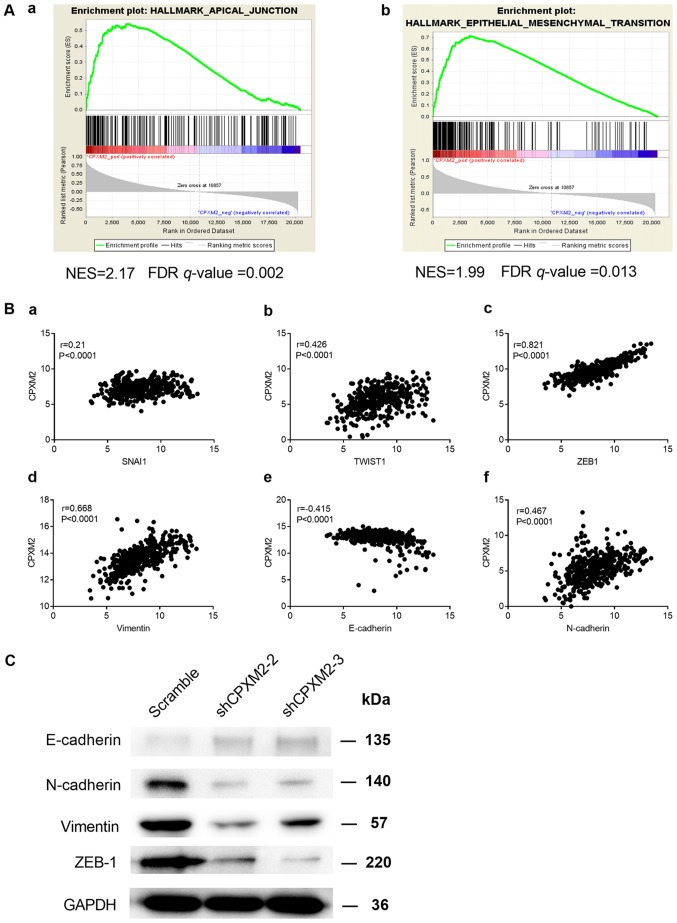
Figure 5.
Potential involvement of CPXM2 in the regulation of EMT. (A) GSEA enrichment plots indicate that CPXM2 expression was positively correlated with apical junction and EMT gene signatures. High CPXM2 expression in GC patients was positively correlated with the (a) HALLMARK_APICAL_JUNCTION and (b) HALLMARK_EPITHELIAL_MESENCHYMAL_TRANSITION gene sets. (B) CPXM2 was significantly correlated with several key genes associated with EMT: (a) SNAI1, (b) TWIST1, (c) ZEB1, (d) vimentin, (e) E-cadherin and (f) N-cadherin. (C) Western blotting analysis was used to compare expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers between GC cells infected with shCPXM2 or scramble. GAPDH was used as loading control. CPXM2, carboxypeptidase X, M14 family member 2; FDR, false discovery rate; GC, gastric cancer; EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis; NES, normalized enrichment score.