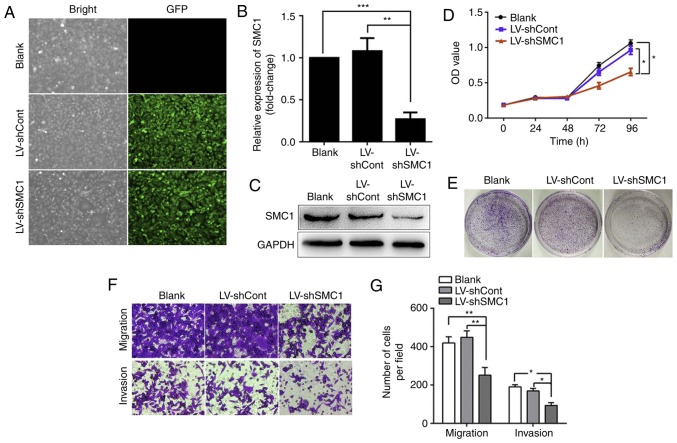
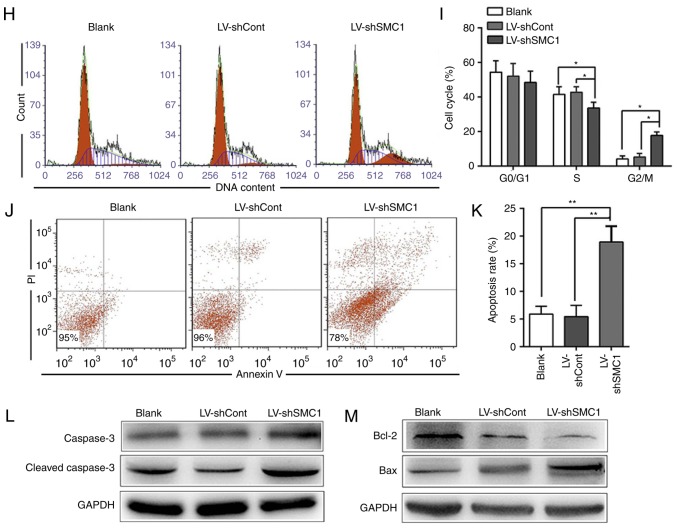
Figure 2.
Knockdown of SMC1 inhibits malignant phenotypes and induces apoptosis in SW620 cells. (A) LV infection efficiency in SW620 cells. (B) Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis of SMC1 mRNA levels in SW620 cells. (C) Western blot analysis of SMC1 protein levels in SW620 cells. (D) In vitro growth curves of SW620 cells transfected with lentivirus. Cell viability was determined by MTT assays, and the OD was detected at 450 nm. (E) Colony formation of SW620 cells following lentiviral transduction. (F and G) Migratory and invasive abilities of SW620 cells following SMC1 knockdown were determined by Transwell assays. Cells were counted in 4 random fields (magnification, ×400). (H) Knockdown of SMC1 induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase in SW620 cells. (I) Quantitative analysis of the cell cycle distribution of SW620 cells. (J and K) Apoptosis of SW620 cells following SMC1 knockdown was measured via flow cytometry. (L and M) Western blot analysis of the expression of apoptosis-associated molecules, including caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3 and Bcl-2/Bax. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Cont, control; LV, lentivirus; OD, optical density; PI, propidium iodide; sh, short hairpin (RNA); SMC1, structural maintenance of chromosomes 1.