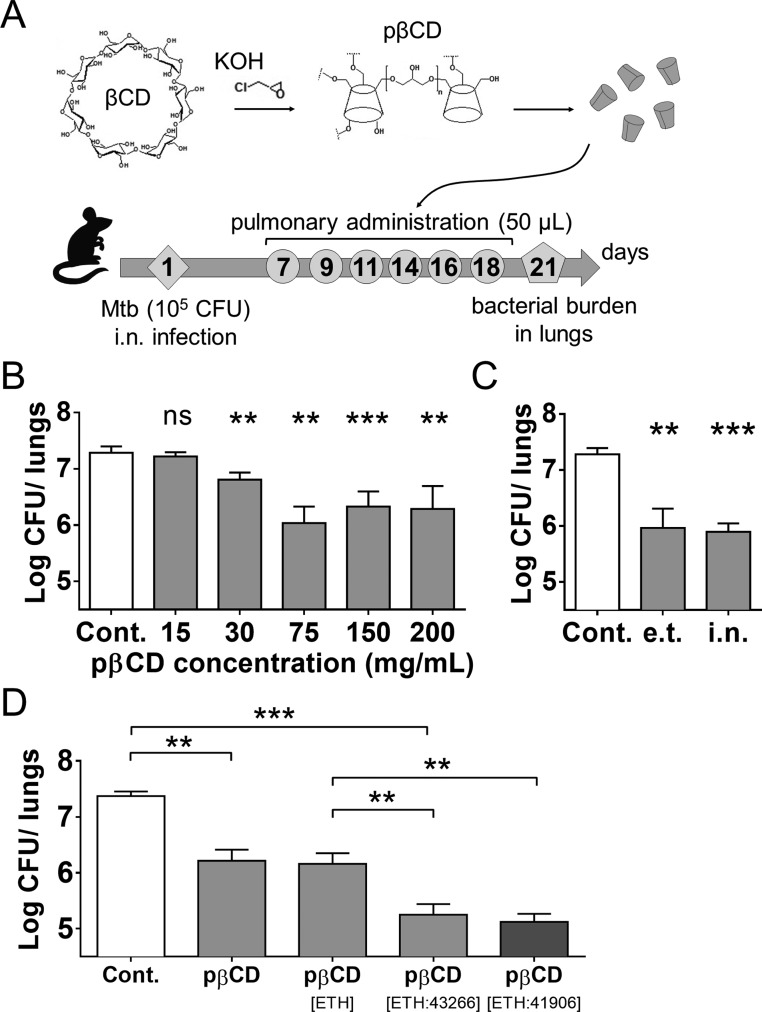
Figure 1.
Assessment of the effect of pβCD on the lung mycobacterial load in Mtb-challenged mice. (A) Experimental design: BALB/c mice were anesthetized and i.n. inoculated with 105 CFU of Mtb H37Rv strain contained in 20 μL of PBS. At days 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, and 18 postchallenge, mice received administrations of 50 μL of pβCD of various concentrations via the e.t. route by use of a microsprayer device that generated aerosolization directly into the lungs. At day 21 postchallenge, lungs were harvested for determination of bacterial burden by CFU counting. (B) Mice received 6 inoculations of 50 μL of pβCD preparations at defined concentrations by the e.t. route before pulmonary bacterial load was evaluated at day 21 postchallenge. (C) Comparison of the impact of pβCD (6 × 50 μL at 150 mg/mL) on Mtb pulmonary load administrated by the i.n. route or by the e.t. route after i.n. infection. (D) Comparison of the effect of the administration of unloaded pβCD and pβCD loaded with ETH alone, [ETH:BDM43266] or [ETH:BDM41906] (6 × 50 μL at 150 mg/mL of pβCD). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are representative of at least two independent experiments. Symbols ** and *** denote p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively.