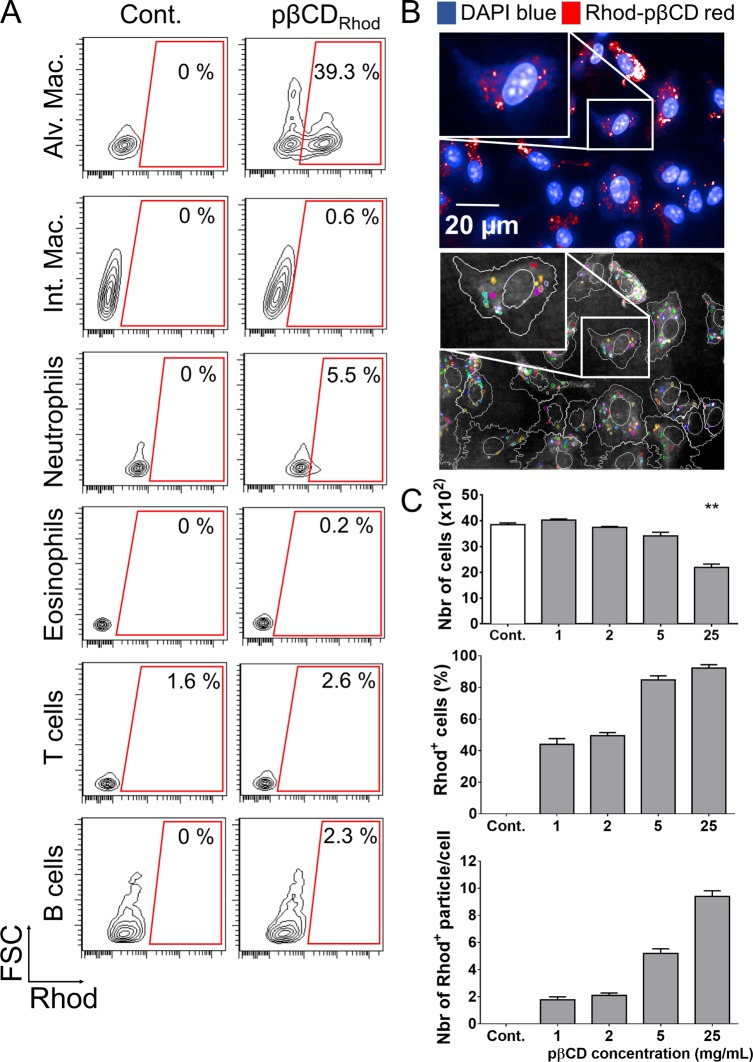
Figure 2.
pβCD invade preferentially alveolar macrophages. (A) BALB/c mice received one e.t. administration of rhodamine-coupled pβCD (50 μL of 150 mg/mL) and were euthanized 2 h postadministration to identify cells that internalized nanoparticles by flow cytometry. The following cell types were discriminated: alveolar macrophages (CD11c+ F4/80+ SiglecF+), interstitial macrophages (F4/80+ CD11cint SiglecF–), neutrophils (CD11b+ Ly6G+), eosinophils (SiglecF+ CD11c–), T cells (CD3+), and B cells (B220+ MHCII+). Data represent FSC vs Rhod plots of selected populations of one representative mouse in two independent experiments. (B, top image) BMDM originated from BALB/c were incubated 24 h with rhodamine-coupled pβCD before fixation and staining with DAPI in order to label the nuclei for confocal microscopy (scale bar: 20 μm). (B, bottom image) Using Columbus software, images were segmented to delimit cells (white) and Rhod+ pβCD (color). (C) Fields were analyzed to quantify the total number of cells, the percentage of cells interacting with pβCD, and the number of nanoparticles per cell. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments. ** denotes p < 0.01.