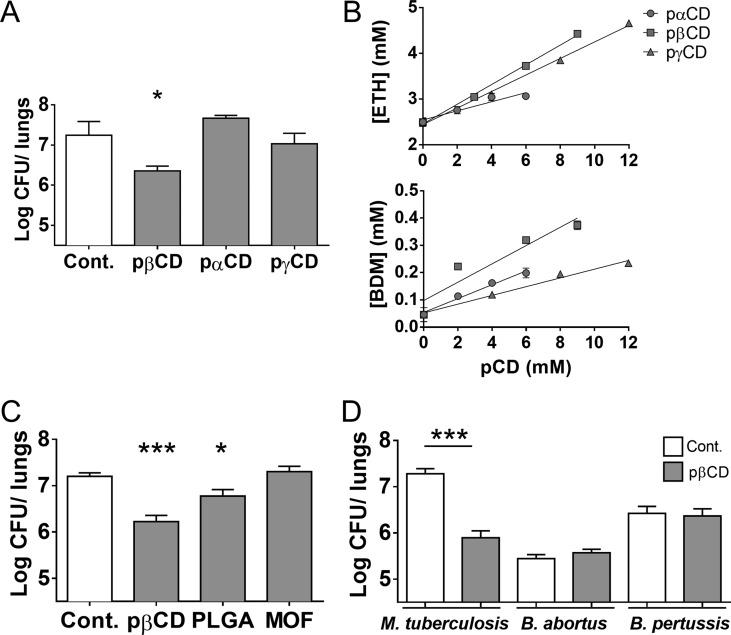
Figure 7.
Effect of other types of nanoparticles on Mtb infection and effect of pβCD on other bacterial pulmonary diseases in mice. (A, C) BALB/c mice were infected via the i.n. route with 105 Mtb H37Rv (20 μL of PBS). At days 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, and 18 mice received pulmonary administration of nanoparticles in a volume of 50 μL (pαCD, pβCD, or pγCD 150 mg/mL, PLGA 15 mg/mL, MOF 5 mg/mL) 21 days postinfection. Lungs were harvested for bacterial burden evaluation by CFU counting. (B) Solubility properties of ETH and BDM43266 using pαCD, pβCD, and pγCD. (D) Mice were i.n. infected with the indicated bacteria. At defined days postinfection, mice received i.n. administration of pβCD (150 mg/mL, 50 μL) before CFU counting. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments. Symbols * and *** denote p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively.