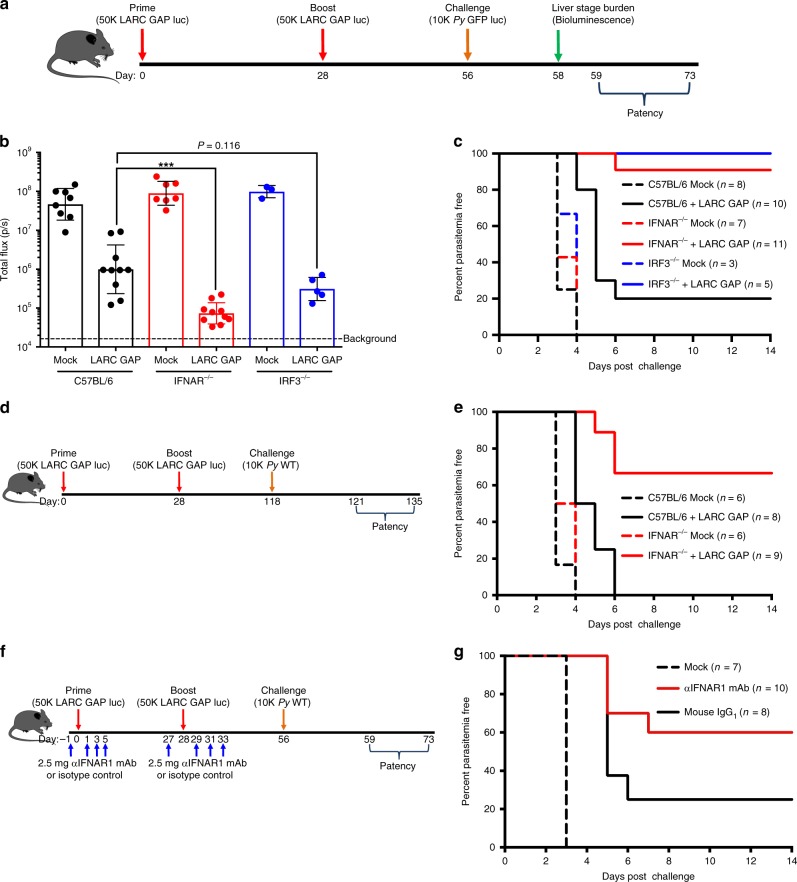
Fig. 1.
Ablation of type I IFN signaling enhances protection against pre-erythrocytic Plasmodium infection in LARC GAP-immunized mice. a Schematic of the immunization regimen. Mice were immunized twice with 50,000 LARC GAP sporozoites and then challenged with 10,000 Py GFPluc sporozoites 1 month after the final immunization. b Quantification of bioluminescent LS parasite burden 44 h after challenge. LS burden is significantly reduced in the livers of immunized WT B6 mice and further reduced in IFNAR−/− mice and IRF3−/− mice. c Examination of blood stage infection in immunized mice after sporozoite challenge 30 days post last immunization. d Schematic of the immunization regimen with first challenge at 90 days after the last immunization. Mice were immunized with LARC GAP sporozoites using the immunization regimen outlined in a and challenged with Py WT sporozoites 3 months after the last immunization. e Examination of blood stage infection in immunized mice after sporozoite challenge 90 days after thelast immunization. f Schematic of GAP-immunization regimen after treatment with αIFNAR1-blocking mAbs. g Examination of blood stage infection in B6 immunized mice treated with an IFNAR1-blocking mAb or isotype control antibody and challenged with WT sporozoites 30 days after the last immunization. Data from panels b, c, e and g are compiled from two independent experiments with at least two mice in each group per experiment. Each dot represents a single mouse. Bar graphs are expressed as mean ± SD. Total number of mice in each experiment is shown in the survival curves. ***p < 0.0001 (from unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). Components of this figure were created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com