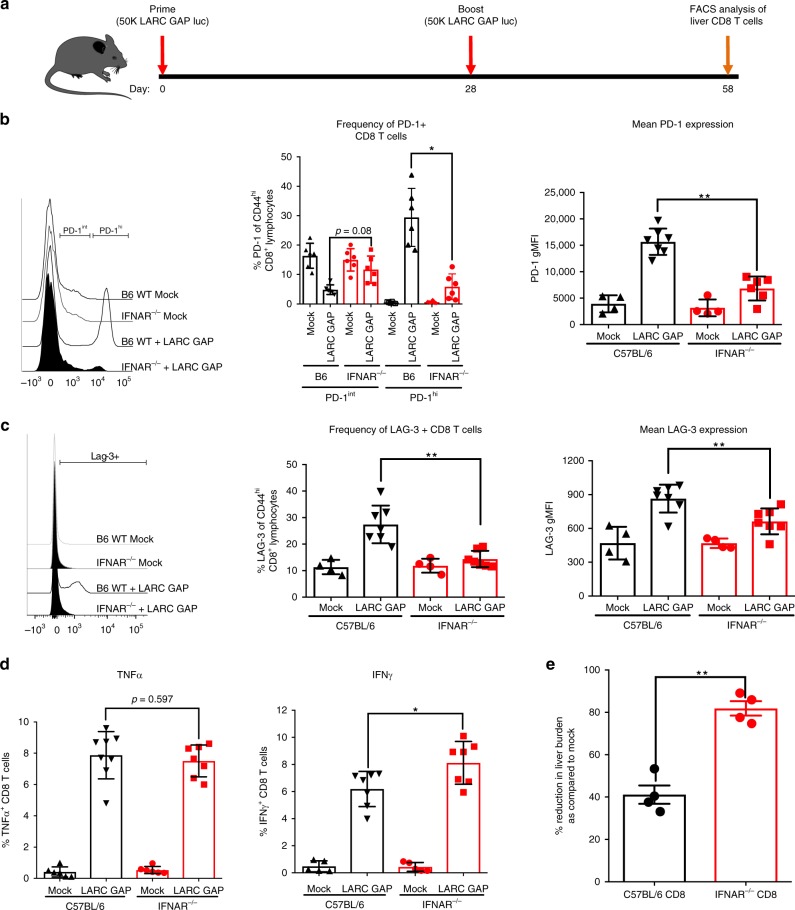
Fig. 4.
Type I IFN signaling increases CD8 T cell exhaustion and memory T cell turnover in LARC GAP-immunized mice. a Schematic of the immunization regimen. B6 mice and IFNAR−/− mice were immunized twice with 50,000 LARC GAP sporozoites. Thirty days after the second immunization, liver leukocytes cells were isolated and subjected to FACS analysis. b Expression of the co-inhibitory marker PD-1 is reduced on liver CD8 T cells isolated from immunized IFNAR−/− mice when compared to immunized WT B6 mice. PD-1+ cells are defined as PD-1hi/intCD44hi of CD8+CD4−CD3+ T lymphocytes. c Expression of the co-inhibitory marker LAG-3 is reduced on liver CD8 T cells isolated from immunized IFNAR−/− mice when compared to immunized B6 mice. LAG-3+ cells are defined as LAG-3+CD44hi of CD8+CD4−CD3+ T lymphocytes. d FACS analysis of ex vivo-stimulated liver CD8 T cells isolated from immunized B6 mice and immunized IFNAR−/− mice. The proportion of TNFα and IFNγ was quantified in enriched CD8 T cells. e Adoptive transfer of 2.5 × 106 liver CD8 T cells isolated from immunized B6 or immunized IFNAR−/− mice and subsequently transferred into naïve B6 mice prior to challenge with 1500 Py GFPluc sporozoites. Data from panels b and c are compiled from two independent experiments with two mock immunized and three LARC GAP immunized mice in each group. Bar graphs are expressed as mean ± SD. Data from panels d and e represent one of two independent experiments. Each dot represents a single mouse. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.005 (from unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). Components of this figure were created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com