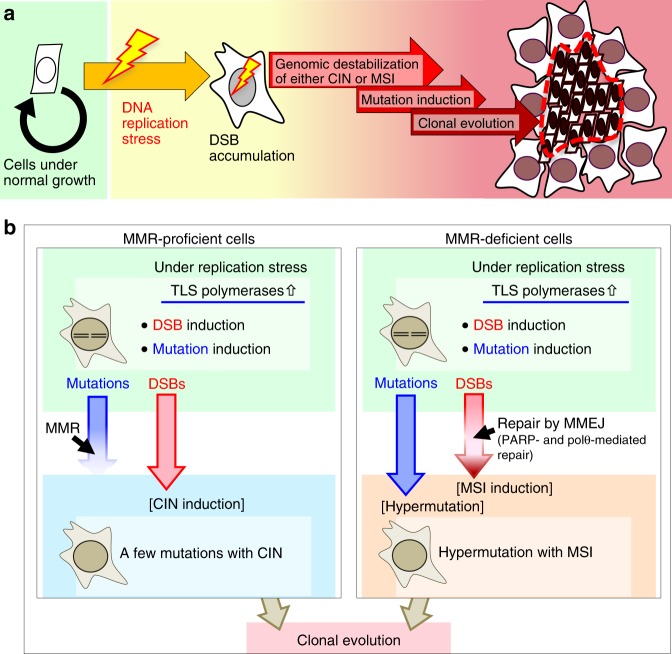
Fig. 7.
Model. a Cells that accumulate replication stress-associated DSBs are at a higher risk of genomic destabilization of either CIN or MSI. Genomic destabilization is associated with induction of mutations, leading to clonal evolution of cells with defects in cellular defense systems. b CIN is caused when replication stress-associated DSBs are not repairable, whereas MSI arises in association with erroneous DSB repair by MMEJ. Hypermutation is also induced in MMR-deficient cells