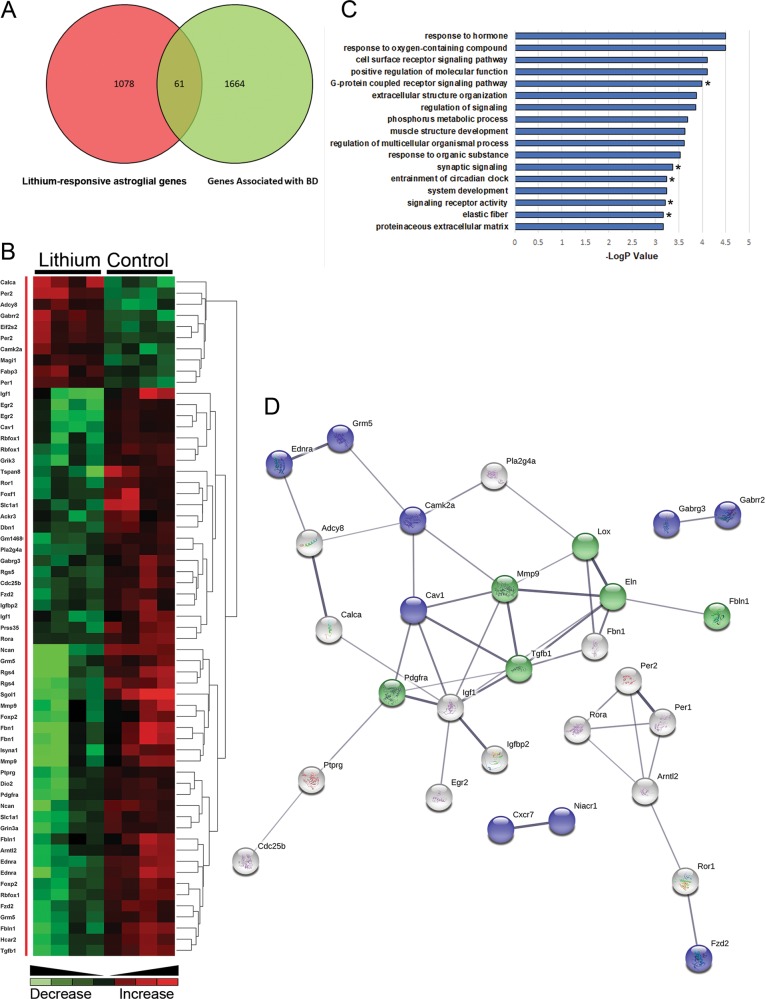
Fig. 2. Lithium-responsive astroglial genes associated with bipolar disorder (BD).
a Interrogation of lithium-responsive astroglial genes against BD databases DISGENET(5.0) and BDGene34,35 identified 61 potential outcome markers that are present in both groups. b Unsupervised hierarchical clustering illustrates the overriding effect of lithium to downregulate BD-associated astroglial genes. c GO analysis identifies receptor signalling and ECM organisation as major astroglial biological processes regulated by lithium and associated with BD; Tgfb1 was found in all the GO terms apart from the five indicated with asterisks. d NEST analysis of lithium-responsive astroglial genes associated with BD predicted a major interaction between LOX and Elastin with TGFβ1 and MMP9 as the mechanism for astroglial ECM regulation and potential surrogate markers in BD (PPI enrichment p = 9.55e−15 p < 0.001; coloured nodes represent top biological pathways: green = ECM organisation (p < 0.001), blue = G-protein couple receptor signalling (GPCR) pathways (p < 0.001)