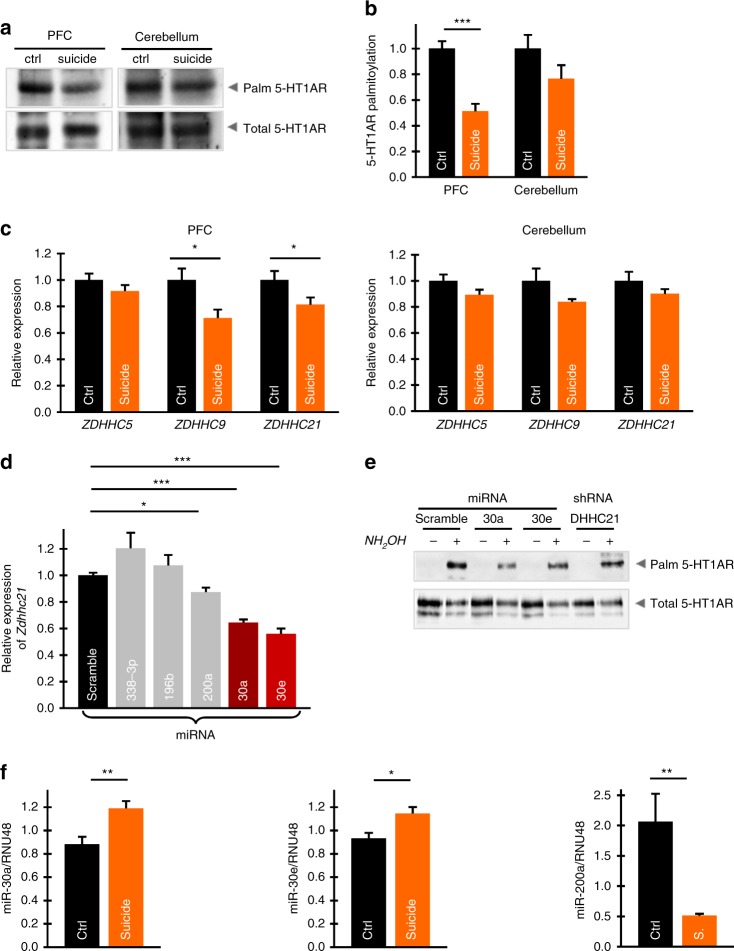
Fig. 6.
Attenuated 5-HT1AR palmitoylation in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of individuals with major depressive disorder (MDD) who died by suicide correlates with reduced expression of ZDHHC21. a 5-HT1AR palmitoylation in the PFC and cerebellum from the control and individuals with MDD who died by suicide (PFC, n = 5; cerebellum, n = 4). b Normalized level of 5-HT1AR palmitoylation in the PFC and cerebellum of individuals with MDD who died by suicide in comparison with control subjects (two-tailed t test; see also Supplementary Fig. 8). c Relative expression levels of ZDHHC5, -9, and -21 in the PFC (left) and cerebellum (right) of control (n ≥ 14) and individuals with MDD who died by suicide (n ≥ 12). Data points represent the means ± SEM (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t test). d N1E cells were transfected with microRNAs as indicated and the expression of ZDHHC21 was determined by reverse transcriptase-PCR (see also Supplementary Table 1). Data points represent mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t test). e N1E cells were transfected with 5-HT1AR along with miR-30e, miR30-a, or shRNA against ZDHHC21. Palmitoylation of 5-HT1AR was analyzed by acyl-biotinyl exchange. Western blots shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. f Analysis of miR-30a, -30e, and -200a expression in the PFC of control and individuals with MDD who died by suicide. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two-tailed t test). Source data are available as a Source Data file