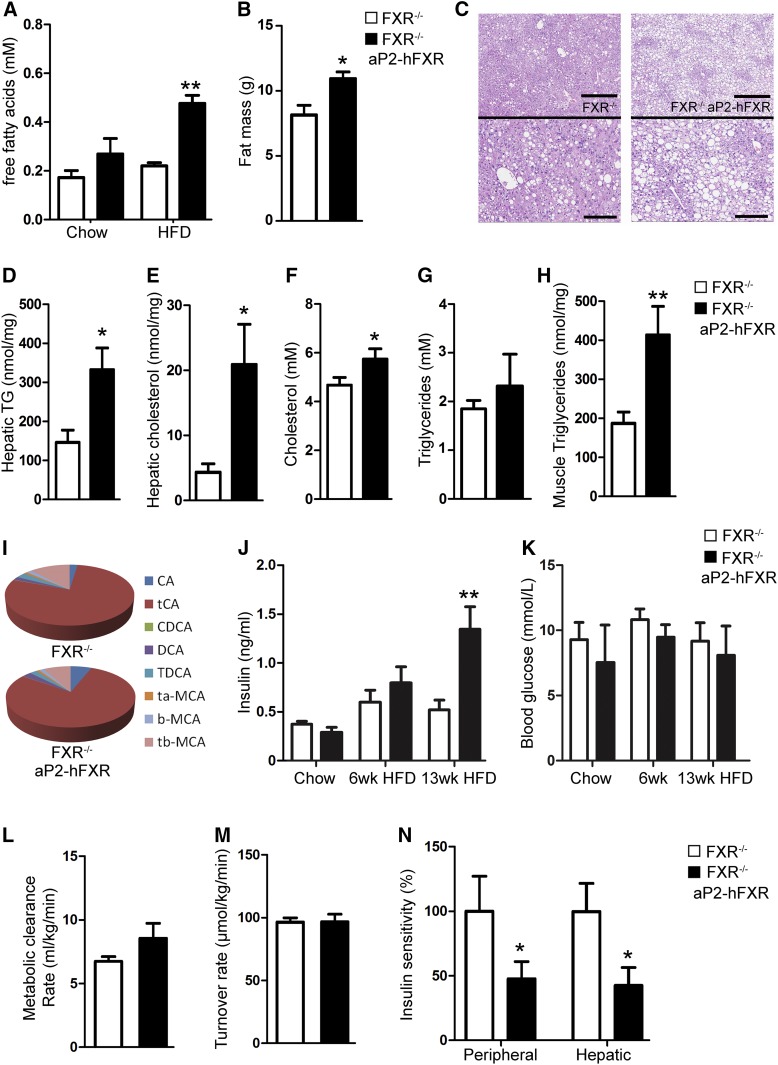
Fig. 6.
Obesogenic conditions induce ectopic lipid accumulation and insulin resistance in aP2-hFXR mice. A: Plasma free fatty acid levels of chow- and HFD-fed FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice. B: Fat mass of FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice after 3 months of HFD. C: Liver H&E staining showing lipid accumulation that is most apparent in the pericentral zone. Top scale bars in panel C depict 500 μm, bottom scale bars in enlargements depict 200 μm. Hepatic triglycerides (D) and hepatic total cholesterol (E) of FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice after prolonged HFD. Plasma total cholesterol (F) and triglycerides (G) of FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice after 3 months of HFD. Gastrocnemius triglycerides of FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice after 3 months of HFD (H) and plasma bile acid composition (I). (J) Four hour-fasted plasma insulin (J) and blood glucose (K) of chow- and HFD-fed FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice. Metabolic clearance rate (L), turnover rate (that under these conditions equals glucose production) (M), and peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity (N) during a whole-body glucose test of FXR−/− and FXR−/− aP2-hFXR mice after 3 months of HFD (n = 6–8 per group; data are represented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.