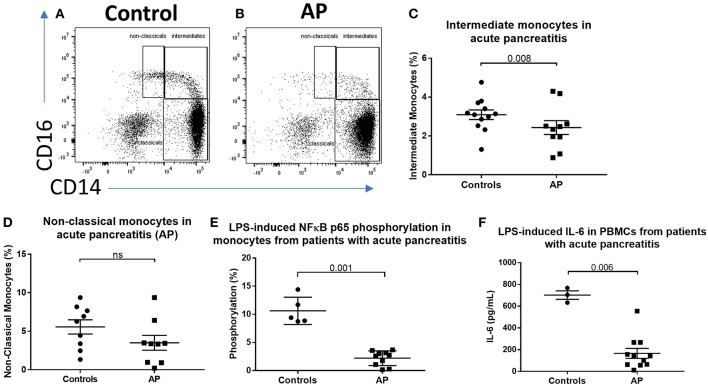
Figure 1.
CD16+ monocytes are reduced in acute pancreatitits and in response to LPS. Representative flow cytometry plots showing monocyte subsets in (A) healthy controls or (B) patients with acute pancreatitis (AP). Monocytes were identified by forward and side scatter, HLA-DR positivity and classified according to the expression of CD14 and CD16. (C) Proportion of intermediate monocytes was significantly reduced in patients with AP compared with controls (p = 0.008). (D) Proportion of non-classical monocytes was reduced in patients with AP compared to controls [3.4 vs. 6.3% (E)]. Patients with AP had reduced levels of NFκBp65 phosphorylation at S529 in monocytes stimulated with LPS compared with controls (p = 0.001, percentage increase over unstimulated baseline). (F) Patients with AP had reduced LPS-induced IL-6 production from PBMCs compared to controls (p = 0.006).