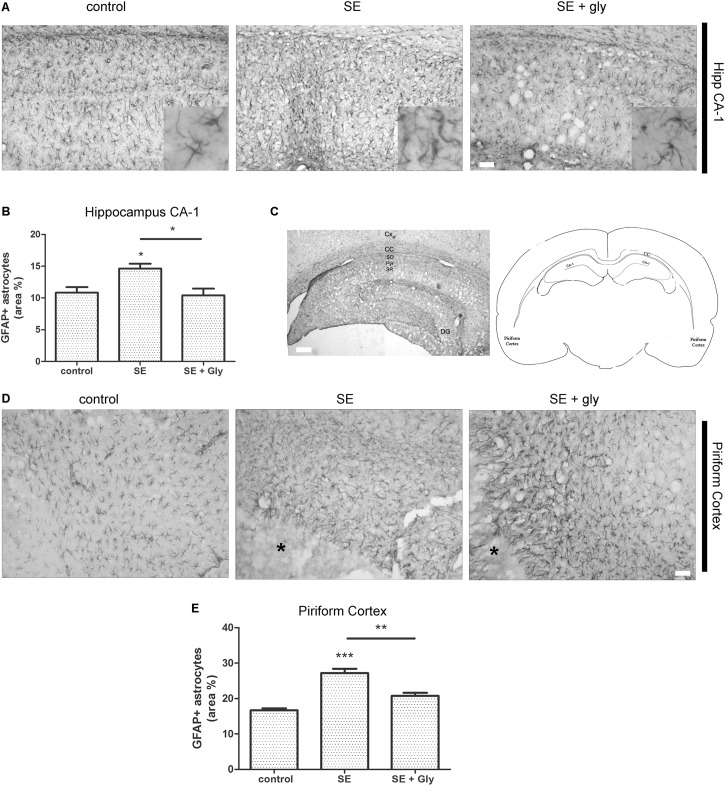
FIGURE 8.
HMGB-1 antagonist glycyrrhizin reduces reactive astrogliosis after pilocarpine-induced SE. Rats were exposed to pilocarpine-induced SE, treated with glycyrrhizin or vehicle for 4 days and analyzed after 15 days. (A) Representative images of GFAP-immunostained astrocytes showing the CA-1 hippocampal area. The insets depict astroglial cell morphology in detail. Note the increased astroglial hypertrophy with enlarged projection and increased soma size in SE-exposed animals and the decreased hypertrophy in SE glycyrrhizin-treated animals. Scale bar: 30 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of the GFAP + astroglial cell morphology in the hippocampus of control, SE and SE animals treated with glycyrrhizin. (C) Low magnification of the GFAP-immunostained hippocampus to visualize the different regions (scale bar: 300 μm) and a schematic representation of the analyzed areas in a coronal rat brain section. Cx, Brain cortex; CC, Corpus Callosum; DG, Dentate Gyrus; CA-1, Hippocampal CA-1 area; SR, Stratum Radiatum; SO, Stratum Oriens; Pyr, Pyramidal neurons. (D) Representative images of GFAP-immunostained astrocytes in the piriform cortex. Note the necrotic core (∗) that is characteristic of SE-exposed animals surrounded by highly hypertrophied astrocytes. Scale bar = 35 μm. (E) Quantitative analysis of GFAP-immunostained cell area in the piriform cortex and hippocampus of control, SE and SE animals treated with glycyrrhizin. Statistical analyses were performed by one way ANOVA and Student Newman–Keuls post-test, with statistical significance represented as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Control animals were exposed to lithium chloride and saline was used as vehicle. The number of animals were n = 6 per experimental group.