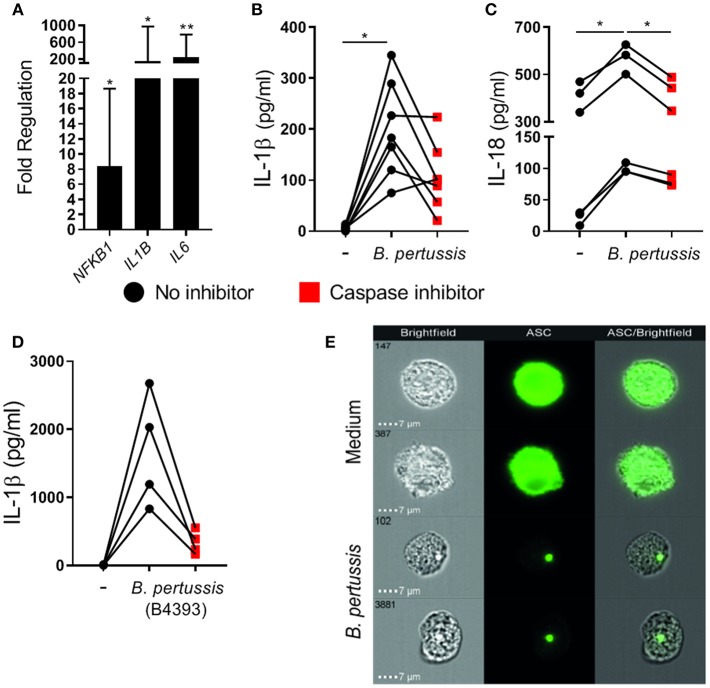
Figure 2.
B. pertussis induces inflammasome activation in primary human mo-MΦ. (A) Mo-MΦ were stimulated with B. pertussis (Tohama I, MOI = 100) for 6 h after which the transcription levels of inflammasome associated genes were determined using reverse transcriptase qPCR. Data is expressed as mean fold change of three donors calculated as the transcription levels relative to the transcription levels in untreated mo-MΦ. (B) The levels of IL-1β (n = 7) and (C) IL-18 (n = 6) released into the supernatant by mo-MΦ stimulated with B. pertussis for 22 h in the presence (red squares) or absence (black dots) of a caspase inhibitor (Tohama I, MOI = 10). (D) IL-1β secretion of mo-MΦ stimulated with a clinical B. pertussis strain (B4393, MOI = 10) in de presence (red squares) or absence (black dots) of a caspase inhibitor. Black dots and red squares represent values of individual donors. (E) Representative images of the cellular ASC (green) distribution as determined by flow imaging of untreated mo-MΦ or mo-MΦ stimulated with a clinical B. pertussis strain (B4393, MOI = 100). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.