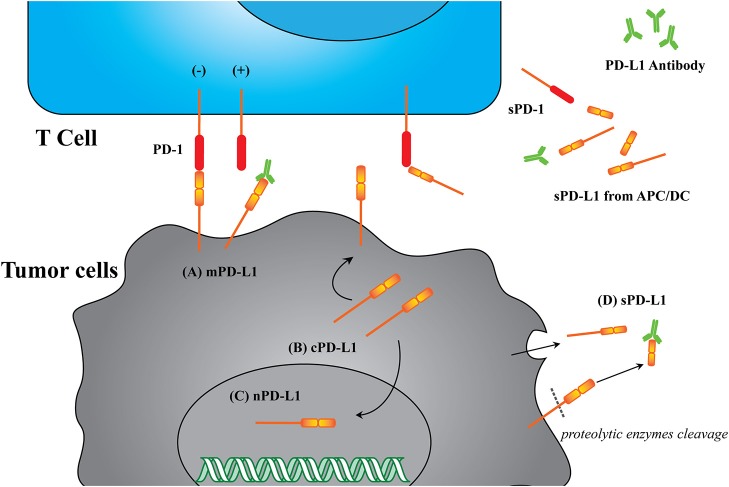
Figure 2.
Illustration of different PD-L1 formats. (A) mPD-L1, located on the tumor cell membrane, is able to bind with PD-1 on T cells and response to tumor immune escape. PD-L1 antibody competitively binding to mPD-L1 breaks the tolerance, leading to tumor cell clearance. (B) cPD-L1 is located in cytoplasm, and potentiates to transfer to mPD-L1. (C) nPD-L1 is located in nuclei. Its aberrant upregulation is speculated to be associated with promoted cell chemo-resistance. (D) sPD-L1 refers to its soluble format in the serum, generated from either endogenous secretion or cleaved fraction of mPD-L1s. Both host cells (such as APC and DC) and tumor cells can be the source of sPD-L1. PD-L1 antibody therapeutic effect is limited to sPD-L1 consumption, and cannot modulate intracellular PD-L1.