Figure 6.
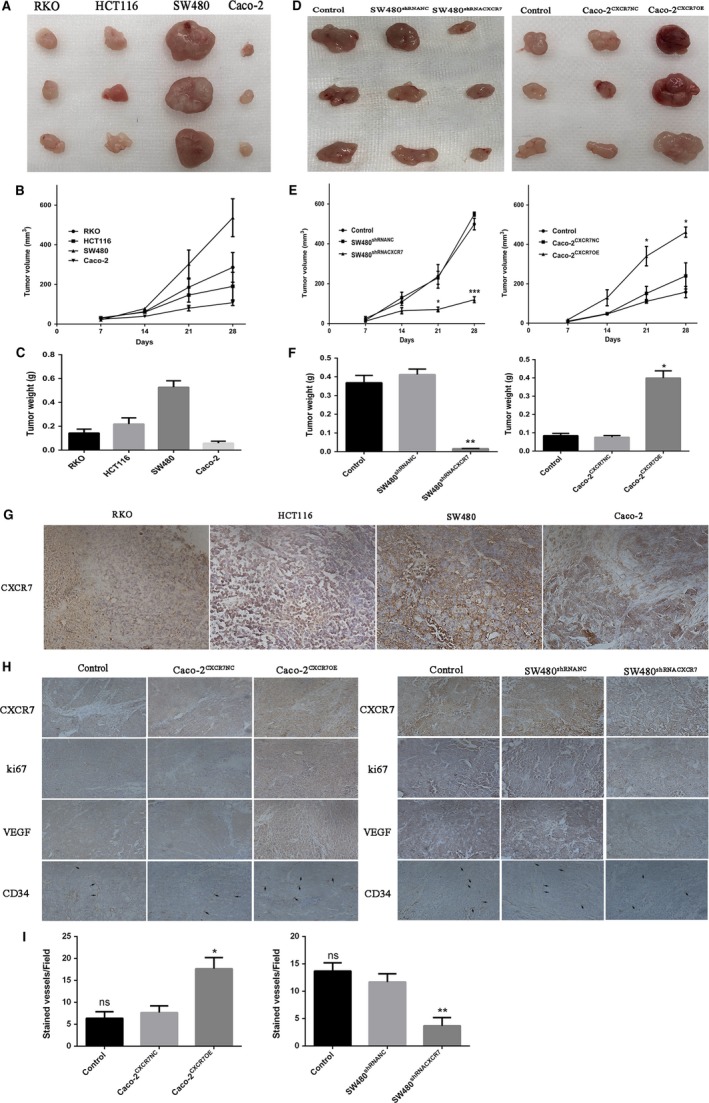
Effect of CXCR7 on tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo Notes: A, Picture of RKO, HCT116, SW480 and Caco‐2 tumor tissue. B, Tumor volume of RKO, HCT116, SW480 and Caco‐2 groups. C, Tumor weight of RKO, HCT116, SW480 and Caco‐2 groups after sacrifice in mice. D, Left panel: Tumor picture of SW480 cells silencing CXCR7, right panel: Tumor picture of Caco‐2 cells overexpressing CXCR7. E, Left panel: Tumor volume of SW480 cells silencing CXCR7, right panel: tumor volume of Caco‐2 cells overexpressing CXCR7. F, Left panel: Tumor weight of SW480 cells silencing CXCR7 groups after sacrifice in mice, right panel: Tumor weight of Caco‐2 cells overexpressing CXCR7 after sacrifice in mice. G, Immunohistochemical analysis of CXCR7 in RKO, HCT116, SW480 and Caco‐2 tumor tissues. H, Tumor tissue sections were harvested for immunohistochemical staining of CXCR7, Ki67, VEGF and CD34 in each group. I. The count of CD34 microvessels reflected the MVD values. * P < .05, ** P < .01 and *** P < .001 vs overexpression groups. magnification 200×. Data in each group are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Abbreviations: VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; MVD: microvessel density NC, negative control. ns: No statistical significance
