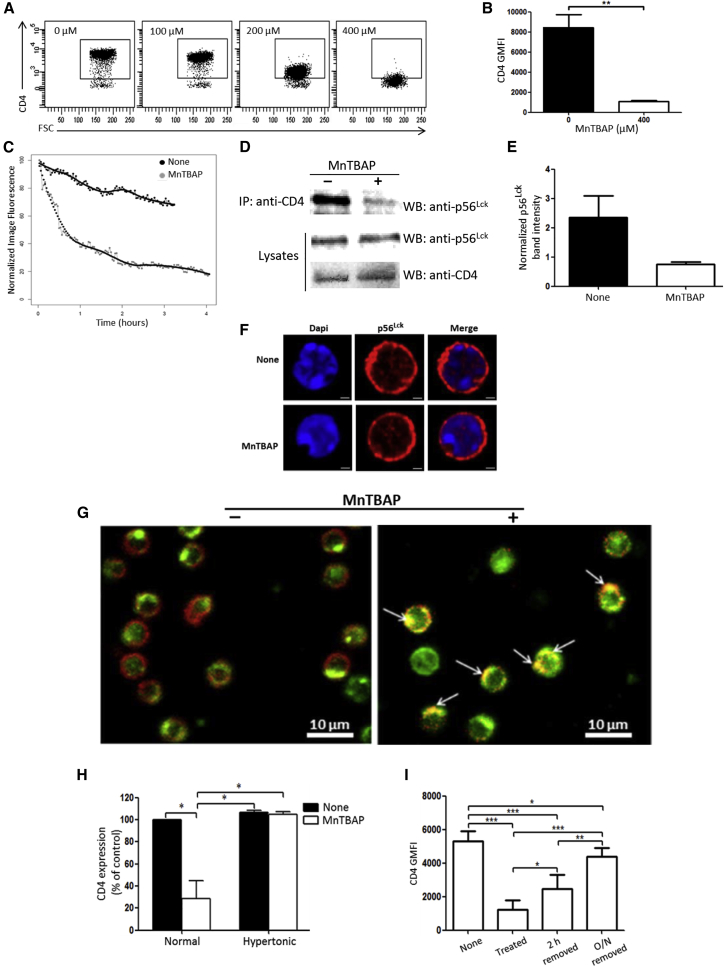
Figure 1.
MnTBAP-Induced CD4 Reversible Internalization Mechanism
(A) CD4+ T cells isolated by negative selection from C57BL/6 mouse splenic cell suspensions were cultured for 2 h in complete medium with increasing doses of MnTBAP (0 to 400 μM), and then analyzed by flow cytometry for CD4 expression on live splenic T cells. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Graph indicating CD4 GMFI (geometric mean fluorescence intensity) on splenic CD4+ T cells after treatment for 2 h with or without MnTBAP at 400 μM. (n = 4 independent experiments). (C) Time-lapse analysis of CD4 cell surface over time decline on CD4+ T cells. After CFSE and CD4 staining, splenic CD4+ T cells were incubated in the absence or presence of MnTBAP and subjected to live-cell time-lapse image acquisition every 120 s for 4 h. CD4 fluorescence intensities, normalized to the maximum fluorescence measured at t0, are reported for each condition. One representative experiment out of two is indicated. (D) MnTBAP induces disruption of the CD4/p56Lck complex. Protein extracts were prepared from splenic CD4+ T cells after treatment for 2 h with or without MnTBAP. Crude extracts were subjected to CD4 immunoprecipitation (IP), followed by western blotting and immunodetection analysis with anti-p56Lck. The p56Lck and CD4 expression levels were also analyzed in whole-cell lysates (Lysates) as controls for the quantities of the proteins of interest before immunoprecipitation. Lysates either in the absence or in the presence of MnTBAP presented approximately equal amounts of p56Lck and CD4. Images are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Graph of p56Lck band intensities detected on CD4 immunoprecipitated materials and normalized with the corresponding band in the lysates. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (F) Confocal microscopy analysis of p56Lck distribution in splenic CD4+ T cells after treatment for 2 h with or without MnTBAP. The red fluorescence (Alexa Fluor 594) signal localizes p56Lck (middle panels), while the blue fluorescence (DAPI) counterstains the nuclei (left panels). Merged images of p56Lck and DAPI-stained nuclei are shown in the right panels. Scale bars, 1 μm. (G) CD4 internalization by a clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Murine splenic CD4+ T cells were cultured for 2 h with or without MnTBAP and then were collected and subjected to immunostaining with anti-CD4 (red signal) and anti-clathrin (green signal) antibodies. Arrows indicate colocalization of CD4 and clathrin resulting in yellow spots. Scale bars, 10 μm. (H) Evidence for clathrin-mediated endocytosis of CD4 molecules. Murine splenic CD4+ T cells were cultured for 2 h with or without MnTBAP in either complete medium (Normal) or hypertonic sucrose medium (Hypertonic) to inhibit specifically clathrine-dependent endocytosis. Cells were then collected and subjected to CD4 cell-surface expression analysis by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as CD4 expression relative to control (complete medium without MnTBAP; Normal), which is defined as 100%. (I) MnTBAP-induced CD4 internalization is reversible. Murine splenic CD4+ T cells were cultured for 2 h with or without MnTBAP. Cells were then stained with Fixable Viability Dye-eFluor 780 (None), stained with anti-CD4-Pacific Blue and fixed (Treated), or washed to remove MnTBAP and put back in culture for either an additional 2 h (2 h removed) or overnight (O/N removed) and finally stained as described earlier and fixed. Fixed cells in all conditions were analyzed by flow cytometry for their CD4 expression, reported on the graph as CD4 GMFI. Cells in the cultures without MnTBAP (None, control) are set at 100% (n = 3 independent experiments). Statistical analyses in (B), (H), and (I) were performed using the Mann-Whitney test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0001.