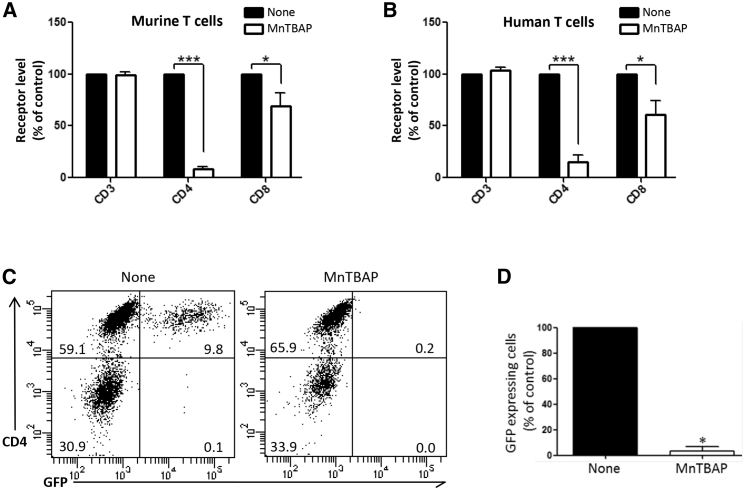
Figure 2.
MnTBAP Induces Dramatic Loss of CD4 on the Surface of Murine and Human T Lymphocytes and Inhibits Transduction of Human T Lymphocytes by Lentiviral Vectors Pseudotyped with gp120HXB2-env
(A and B) MnTBAP effect on murine (A) and human (B) T lymphocyte receptor level. Murine splenic (A) and human peripheral blood (B) cells were treated for 2 h with or without MnTBAP and then analyzed by flow cytometry for cell-surface CD3, CD4, and CD8 expression on live cells. The results of geometric means of fluorescence for each receptor are expressed relative to the corresponding values of the control non-treated cells (None, arbitrarily set at 100%); n = 3–4 independent experiments. For each receptor, statistical comparisons between untreated and treated cells were made using the Mann-Whitney test. (C) CD3+ T cells from human peripheral blood were transduced in the absence or presence of 400 μM MnTBAP on retronectin-coated plates, with gp120HXB2-env pseudotyped lentiviral vectors expressing GFP reporter gene. Transduction efficiency was assessed by flow cytometry via GFP expression 72 h post-transduction. Representative CD4/GFP dot plots are shown, with inset numbers indicating the percentage of cells in each quadrant. (D) Normalized percentages of GFP+ cells obtained 72 h post-transduction. The percentage of GFP+ cells in the cultures without MnTBAP (None, control) is set at 100% (n = 4 independent experiments). Statistical analysis in (D) was performed using paired t test. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.0001.