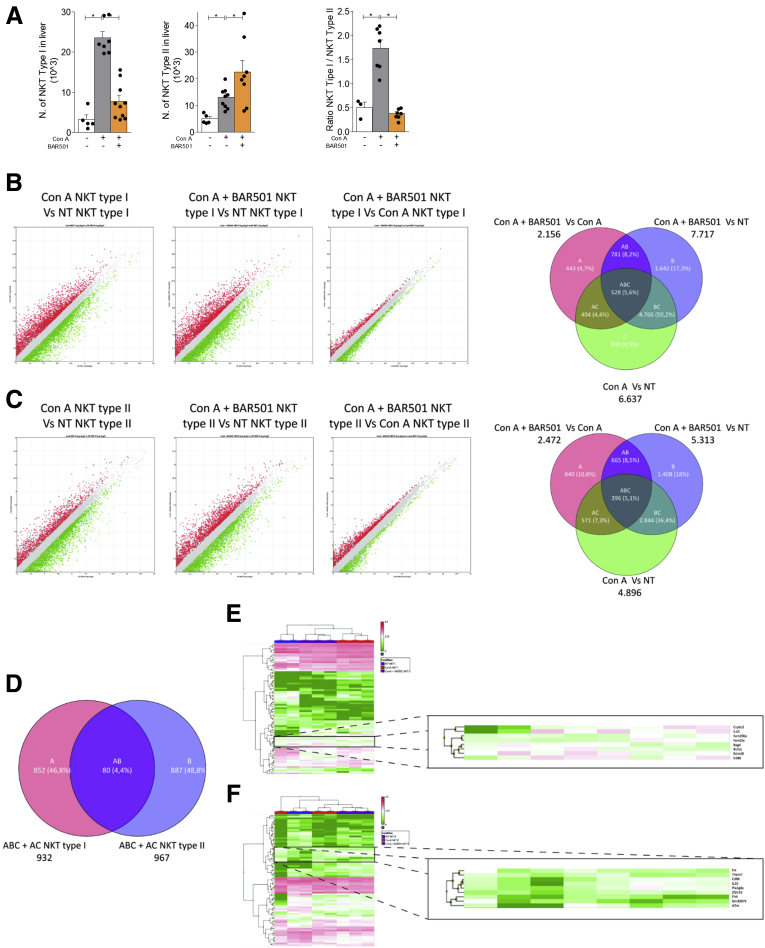
Figure 8.
RNA sequencing of type I and type II NKT cells. Acute hepatitis was induced in C57BL6 male mice GPBAR1+/+ by intravenous injection of Con A (15 mg/kg) and they were sacrificed 24 hours later. Mice were randomized to receive Con A alone or in combination with BAR501 (30 mg/kg) daily from 3 days before induction of hepatitis to the time of the sacrifice. type I and type II NKT cells were purified from the liver of mice with Con A–induced hepatitis, treated or untreated with BAR501. (A) Number of type I NKT (left panel), type II NKT cells (middle panel), and ratio between the number of NKT types I and type II NKT cells (right panel). RNA-seq analysis results in (B) NKT Type I and (C) NKT Type II cells purified from livers of NT, Con A and Con A + BAR501 mice. (B, C) Scatter plots of average gene expression, showing the comparison results of the RNA-seq data with a TAC software analysis; Venn diagram of the number of the differentially expressed genes showing the overlapping regions (identified as ABC, AC, AB and BC sets) between the 3 experimental groups of purified NKT Type I and Type II cells, respectively (Fold Change <-1.5 or >+1.5, p value <0.05). (D) Venn diagrams obtained combining the intersections ABC + AC of NKT Type I and NKT Type II cells, obtained from previous diagrams; from this combination comes out a list of 80 genes (AB), differentially expressed both in NKT Type I and in NKT Type II cells. Clustered heat map of 80 genes (AB) in (E) NKT Type I and (F) NKT Type II cells respectively, with a magnification that highlights a subset of genes including IL-10.