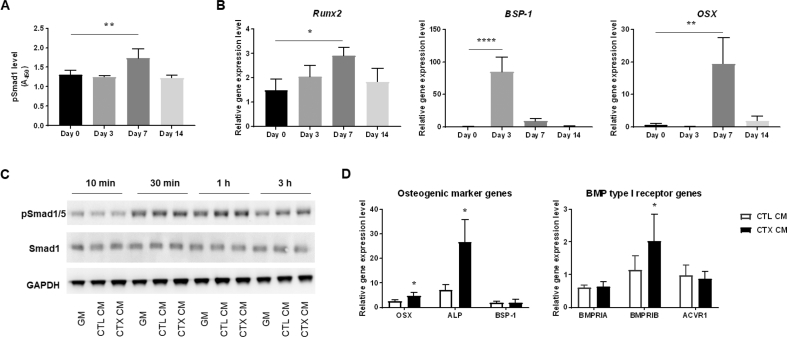
Figure 2.
CTX-induced muscle injury generated an osteoinductive environment. (A) Phosphorylated Smad1 level in muscle tissue lysates measured by pSMAD1 ELISA at different time points after CTX injection demonstrated the activation of BMP signalling (**, p < 0.01; n = 3). (B) PCR analysis showed the upregulation of osteogenic marker gene expression in muscle tissue after CTX injection with the expression of different genes peaking at different time points. (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001; n = 3). Data are normalized to uninjected Day 0 control mice. (C) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Smad1/5 protein and total Smad1 levels revealed the time course of BMP signalling activation in MDSCs cultured in GM and muscle tissue–derived CM. (D) PCR analysis of osteogenic marker gene and BMP type I receptor gene expression in MDSCs. Significantly higher OSX, ALP and BMPR1B expression was detected in MDSCs cultured in CTX CM compared with CTL CM (*, p < 0.05; n = 3). Data are normalized to MDSCs cultured in GM.
BMP = bone morphogenetic protein; CM = conditioned medium; CTX = cardiotoxin; CTL CM, CM derived from control muscle tissue; CTX CM, CM derived from CTX-injured muscle tissue; ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GM = growth medium; MDSCs = muscle-derived stromal cells; PCR = polymerase chain reaction.