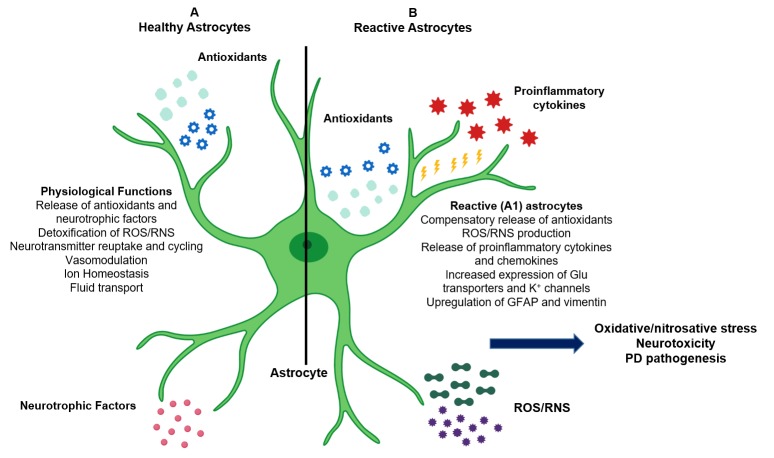
Figure 1.
Role of astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS) and in Parkinson’s disease (PD) pathogenesis. (A) Astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support to neurons, mediate neurotransmission and glutamate transport, and maintain ionic and vascular homeostasis. Astrocytes also secrete endogenous antioxidants (such as glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SODs)) and neurotrophic factors into the extracellular microenvironment and are responsible for detoxification of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) produced as byproducts of metabolism. (B) Reactive astrocytes produce additional antioxidants, proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and ROS/RNS. Chronic reactive astrogliosis leads to astrocytic oxidative/nitrosative stress, neuroinflammation, neuronal apoptosis, and PD pathogenesis.