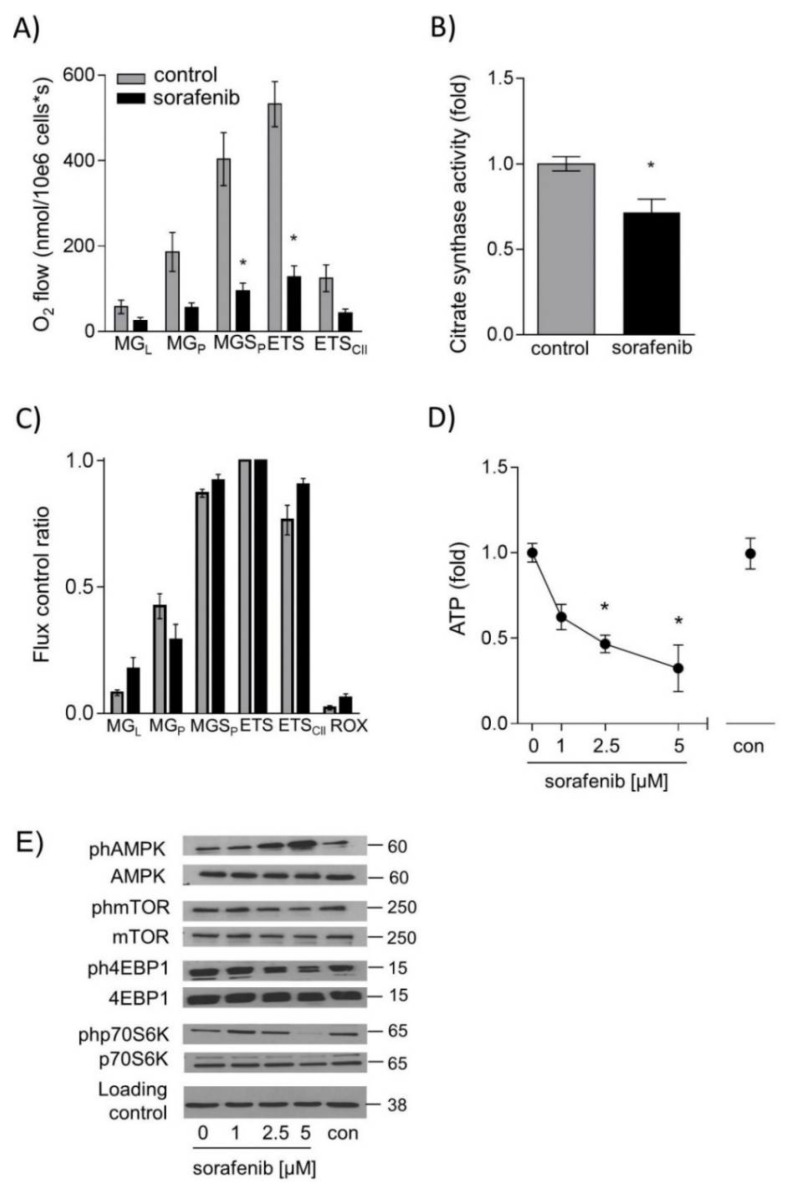
Figure 3.
Sorafenib decreases respiration, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin C1 (mTORC1) pathway in HUH7 cells. Mitochondrial respiration was measured after addition of substrates malate and glutamate (MGL), ADP (MGP), succinate (MGSP), uncoupling by carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone FCCP (ETS), complex I inhibitor rotenone (ETSII) and complex III inhibitor Antimycin A (ROX) by high resolution respirometry (Oxygraph2K, Oroboros, Austria) in (A) permeabilized HUH7 cells (1 µM sorafenib for 24 h) and (C) after direct addition of sorafenib (10 µM) to isolated mitochondria. Values are normalized to maximal O2 flux (uncoupling conditions). (B) Citrate synthase (CS) activity was determined by measuring the conversion of 5,5′-dithio-bis-(2-nitro-benzoic acid) (DNTB) 20 μg of protein were added to 200 μL reaction mix (Tris 20 mM pH 7.5, DTNB 0.1 mM, acetyl-CoA 0.3 mM) and blank absorbance at 412 nm was measured for 15 min at 30 °C. The reaction was started by adding oxaloacetate (0.5 mM), and measurement was continued for 15 min. Blank values were subtracted, and values were normalized to the mean of DMSO controls. (D) ATP levels were measured by CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay after stimulation with sorafenib (1 µM; 2.5 µM, and 5 µM) for 24 h. (E) One representative blot out of three experiments of ph-AMPK, ph-mTOR, ph-4EBP1, and ph-p70S6K is shown. Phosphorylated protein was normalized to total protein and loading control (GAPDH). The mean value of serum-free medium (0 µM) was used to normalize values of the respective datasets. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. con: solvent control (DMSO); * p < 0.05.