Fig. 3. Postmating life-span decrease is mediated by DAF-16, and shrinking correlates with osmotic stress sensitivity.
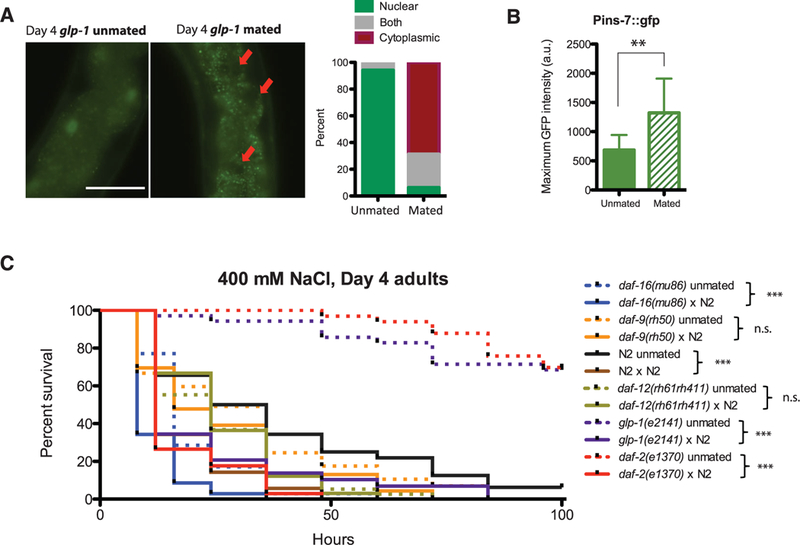
(A) DAF-16::GFP in glp-1 translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm after mating. GFP channel images of glp-1 unmated (left) and mated worms (middle); red arrows point to dark nuclei. Scale bar, 100 μm. (Right) Quantification of GFP localization. (B) Pins-7::gfp expression [maximum ± SD (error bars)] increases significantly in the intestine postmating. a.u., arbitrary units. (C)Survival curves under osmotic stress (400 mM NaCl): Day 1 mated N2 and daf-16(mu86) died faster than the unmated controls put under osmotic stress starting on day 4. Unmated N2: 40.3 ± 6.0 hours, n = 31; mated N2:18.5 ± 1.8 hours, n = 35, P <0.001. Unmated daf-16:19.2 ± 1.9 hours, n = 35; mated daf-16:11.8 ± 1.1 hours, n = 35, P < 0.001. Mated daf-9(rh50) and daf-12(rh61rh411) survived as long as the unmated controls under osmotic stress. Unmated daf-9: 31.2 ± 4.3 hours, n = 30; mated daf-9: 25.7 ± 3.8 hours, n = 23, P = 0.3242. Unmated daf-12: 25.6 ± 2.5 hours, n = 38; mated daf-12: 26.2 ± 2.3 hours, n = 33, P = 0.9714. glp-1 and daf-2 mated worms survive longer than wild type on NaCl, but still die prematurely. glp-1 unmated (n = 35): 131.7 ± 10.4 hours; glp-1 mated (n = 29): 23.2 ± 3.8 hours; P < 0.0001. daf-2 unmated (n = 33): 250.5 ± 30.0; daf-2 mated (n = 34): 17.7 ± 1.8 hours; P < 0.0001. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for all graphs.
