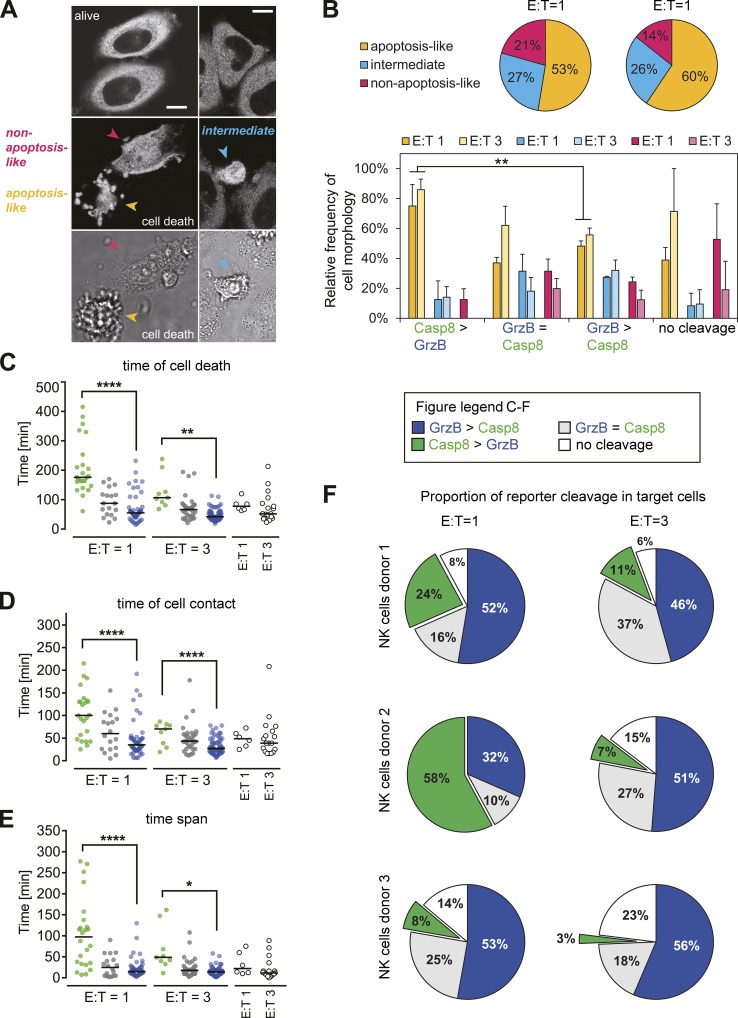
Figure 2.
Cell death morphology, GrzB, and Casp8 activity in target cells killed upon co-culture with primary NK cells. Human primary NK cells were isolated from blood of three healthy donors. For each donor NK cell population, two experiments at different NK cell doses (E/T = 1 and E/T = 3) were performed. HeLa-CD48 target cells expressing the NES-RIEADS-mCherry (GrzB) and NES-ELQTD-GFP (Casp8) reporters were imaged over time by confocal microscopy. (A) Images show alive cells (top) and three different cell death morphologies that were visually distinguished (with reporter fluorescence, center; or transmission light, bottom): an apoptosis-like phenotype with cell blebbing, a non-apoptosis-like phenotype with lack of cell blebbing, and an intermediate phenotype with cell shrinkage but no or few cell blebbing. Scale bars, 10 µm. (B) Pie charts show the frequency of different cell death morphology for cells induced with the three donor NK cells (E/T = 1, in total 94 cells; E/T = 3, in total 119 cells). Bar graphs show this distribution as relative frequencies for cells grouped for the balance of GrzB- and Casp8-reporter cleavage and for E/T ratio (mean ± SEM, n = 3). (C–E) Plots of single cell data of the time of target death (C), the time point of NK cell contact with target cell (D), and the time between NK cell contact and target cell death (E). The median is indicated for pooled data from three independent experiments using NK cells from three donors. (F) Pie charts show the proportion of reporter cleavage at the two different NK cell doses for the NK cells of each donor. ****, P ≤ 0.0001; **, P ≤ 0.01; *, P ≤ 0.05 (unpaired, two-tailed t test with Welch’s correction).