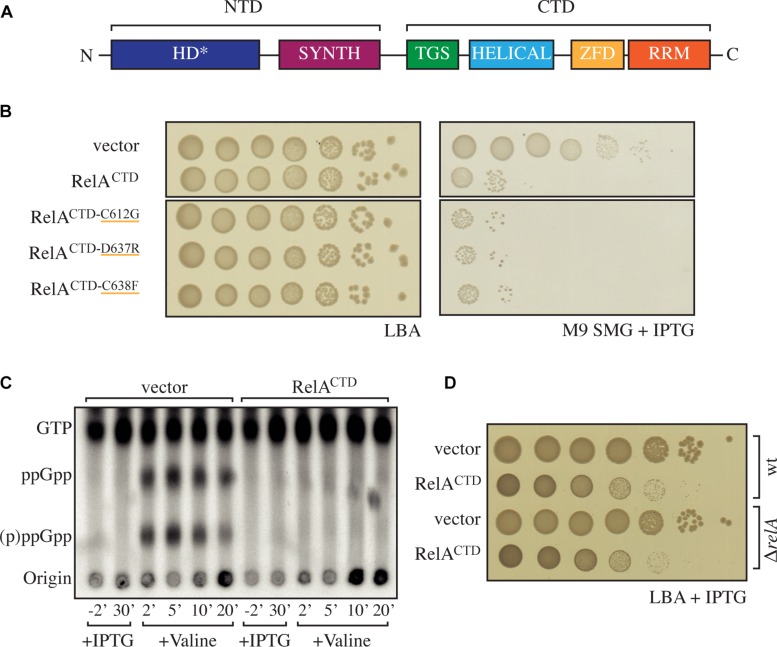
FIGURE 1.
High-level ectopic expression of RelACTD is inhibitory to growth independently of native RelA’s activity. (A) Domain structure of RelA, the enzymatically inactive (p)ppGpp hydrolysis (HD∗) and a functional (p)ppGpp synthesis (SYNTH) NTD domains. TGS (ThrRS, GTPase, and SpoT), Helical, ZFD (Zinc Finger Domain) and RRM (RNA recognition motif) domains comprise the regulatory CTD region. (B) Escherichia coli MG1655 (wt) cells were transformed with high copy IPTG inducible vector, pMG25 (vector), pMG25:relACTD, pMG25:RelACTD–C612G, pMG25:RelACTD–D637R, and pMG25:RelACTD–C638F. The transformed cells were grown at 37°C overnight in M9 minimal medium with 100 μg/ml ampicillin. Ten-fold serial dilutions were made and spotted onto LB agar (LBA) supplemented with 100 μg/ml ampicillin, as a loading control, and onto SMG plates supplemented with 100 μg/ml ampicillin and 1 mM IPTG to induce relA variant expression. (C) Representative audioradiogram of a PEI Cellulose TLC plate showing (p)ppGpp accumulation of E. coli MG1655 carrying pMG25 (vector) or pMG25:relACTD upon valine-induced isoleucine starvation. See section “Materials and Methods” for more details. (D) Overnight cultures of E. coli MG1655 (wt) and MG1655ΔrelA (ΔrelA) transformed with pMG25 (vector) or pMG25:relACTD, grown in LB with 100 μg/ml ampicillin. Ten-fold serial dilutions of were made and spotted onto LB agar supplemented with 1 mM IPTG.