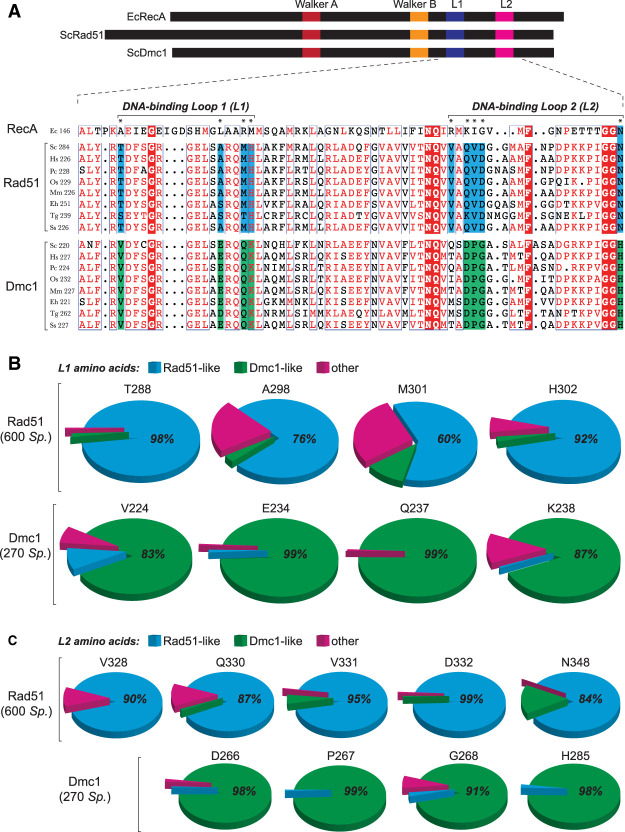
Figure 1.
Identification of Rad51 and Dmc1 L1 and L2 lineage-specific amino acids. (A) Location and sequences of the L1 and L2 DNA-binding loops from RecA, Rad51, and Dmc1. Amino acids conserved in all three lineages are highlighted in red, Rad51 lineage-specific amino acids are highlighted in blue, and Dmc1 lineage-specific amino acids are highlighted in green. Included in the alignments are recombinases from S. cerevisiae, H. sapiens, P. carinii, O. sativa, M. musculus, E. histolytica, T. gondii, and S. scrofa. Asterisks denote L1 and L2 lineage-specific amino acids. (B) Conservation and identity of L1 amino acids based on analysis of 600 Rad51 and 270 Dmc1 sequences. The analyzed positions correspond to ScRad51 amino acids T288, A298, M301, and H302 and ScDmc1 amino acids V224, E234, Q237, and K238. Color-coding indicates Rad51-like, Dmc1-like, and other amino acids (see Supplemental Table S1 for a complete list of all Rad51 and Dmc1 lineage-specific L1 and L2 amino acid residues). (C) Conservation and identity of L2 amino acids.