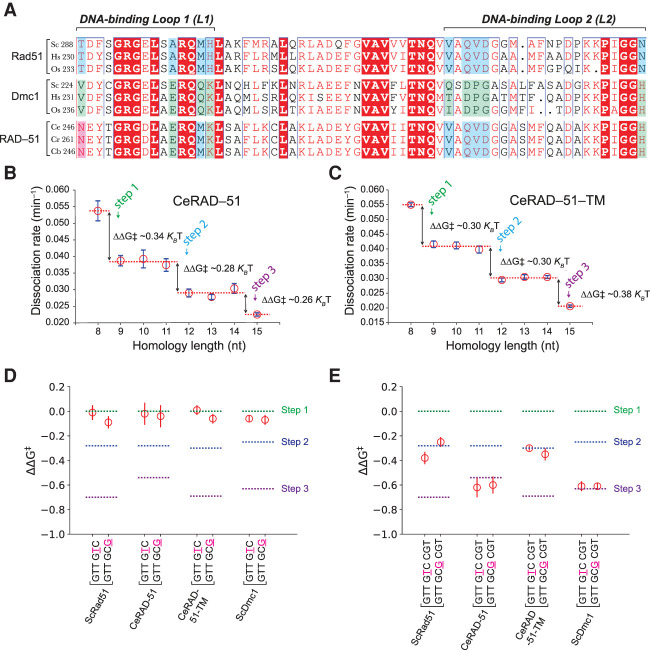
Figure 5.
C. elegans RAD-51 has Dmc1-like amino acids and dsDNA-binding properties. (A) Comparison of Caenorhabditis sp. RAD-51 sequences (C. elegans, Caenorhabditis remanei, and Caenorhabditis brenneri) with Rad51 and Dmc1 sequences from organisms with both recombinases (S. cerevisiae, H. sapiens, and O. sativa). Color-coding is the same as shown in Figure 1A. Base triplet stepping data for wt CeRAD-51 (B) and the CeRAD-51 triple mutant (C). (D) Terminal mismatch triplet assays for CeRAD-51 and CeRAD-51-TM (CeRAD-51 N246S, E256A, K260H triple mutant protein). Data for wt ScRad51 and ScDmc1 are shown for comparison and are reproduced from Figure 3, D and F. (E) Internal mismatch triplet assays for CeRAD-51 and CeRAD-51-TM. Data for wt ScRad51 and ScDmc1 are shown for comparison and are reproduced from Figure 3, D, F, G, and I. In D and E, the free energy changes associated with each step (for fully homologous substrates) are indicated with color-coded dashed lines.