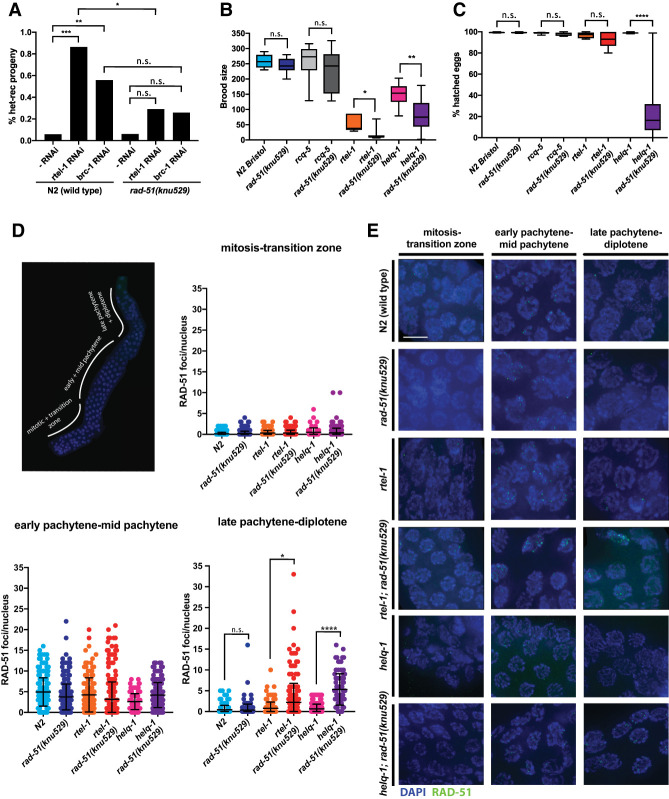
Figure 6.
C. elegans RAD-51 requires Dmc1-like amino acids to avoid formation of toxic HR intermediates during meiosis. (A) Increased recombination between heterologous sequences induced by rtel-1 or brc-1 depletion is suppressed in the rad-51(knu529) background, indicating loss of tolerance for DNA sequence heterology during RAD-51-TM-mediated recombination in vivo. The “-RNAi” label corresponds to conditions in which the C. elegans strain was treated with control bacteria lacking an expression plasmid for RNAi. P-values by χ2. (n.s.) P > 0.05; (*) P ≤ 0.05; (**) P ≤ 0.01; (***) P ≤ 0.001. (B) Brood size in strains of the indicated genotype. Progeny of five to 12 worms were evaluated. P-values by Mann-Whitney test. (n.s.) P > 0.05; (*) P ≤ 0.05; (**) P ≤ 0.01. (C) Percentage of hatched eggs after 24 h in strains of the indicated genotype. Progeny of five to 12 worms were evaluated. P-values by Mann-Whitney test. (n.s.) P > 0.05; (****) P ≤ 0.0001. (D) C. elegans germline with marked zones used to score meiotic RAD-51 focus formation. Quantification of meiotic RAD-51 focus formation in the different zones of the worm germline in strains of the indicated genotype. helq-1; rad-51(knu529) and rtel-1; rad-51(knu529) display persistent RAD-51 foci in late stages of meiosis. Between 67 and 548 cells were quantified for each zone in two independent experiments for each genotype. P-values by Mann-Whitney test. (n.s.) P > 0.05; (*) P ≤ 0.05; (****) P ≤ 0.0001. (E) Representative images of different compartments of the C. elegans germline. (Blue) DAPI staining; (green) RAD-51 staining. Scale bar, 5 µm.