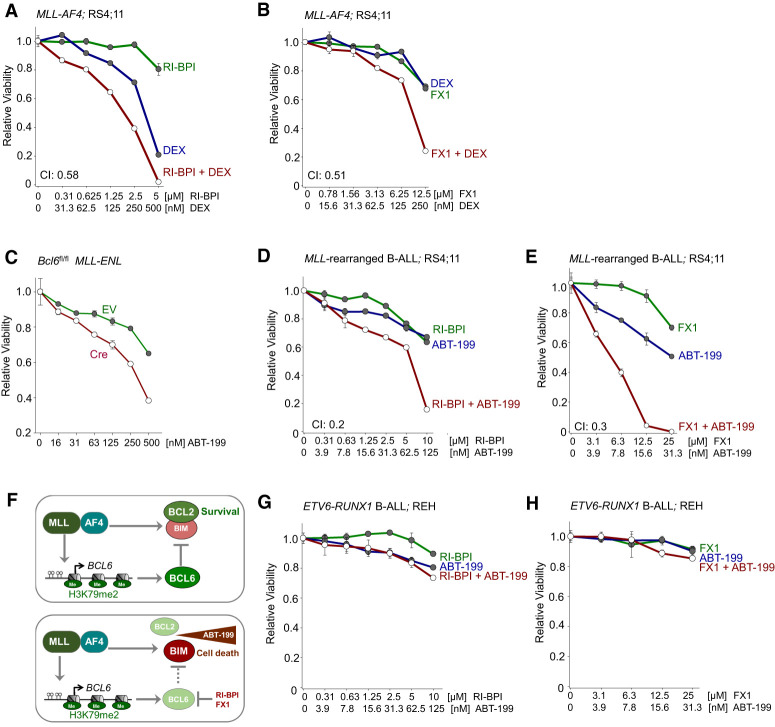
Figure 7.
Dual targeting of BCL2 and BCL6 in MLL-rearranged B-ALL. (A) Human MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells were treated with Dex, RI-BPI, or a combination of both. CI values for ED50 are shown. Relative viability was assessed. n = 3. (B) Human MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells were treated with Dex, FX1, or a combination of both. Relative viability and CI were assessed. n = 3. (C) Relative viability (n = 3) was assessed upon treatment with increasing concentrations of ABT-199 in pre-B cells expressing MLL-ENL following 4-OHT Cre-mediated deletion of Bcl6. (D) Human MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells were treated with ABT-199, RI-BPI, or ABT-199 in combination with RI-BPI. Relative viability and CI were assessed. (E) Relative viability and CI were examined following treatment of human MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells with ABT-199, FX1, or a combination of both. (F) MLL-rearranged fusion proteins induce aberrant expression of BCL6, which contributes to MLL-rearranged-driven leukemogenesis by restricting expression of BIM, a proapoptotic molecule. The BCL2 inhibitor ABT-199 disrupts the interaction between BCL2 and BIM. Pharmacological inhibition of BCL6 (RI-BPI or FX1) synergizes with ABT-199 in eradicating MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells. (G,H) Relative viability was determined upon treatment with increasing concentrations of ABT-199, RI-BPI (G), FX1 (H), or a combination of ABT-199 with RI-BPI (G) or FX1 (H) in ETV6-RUNX1 B-ALL cells.