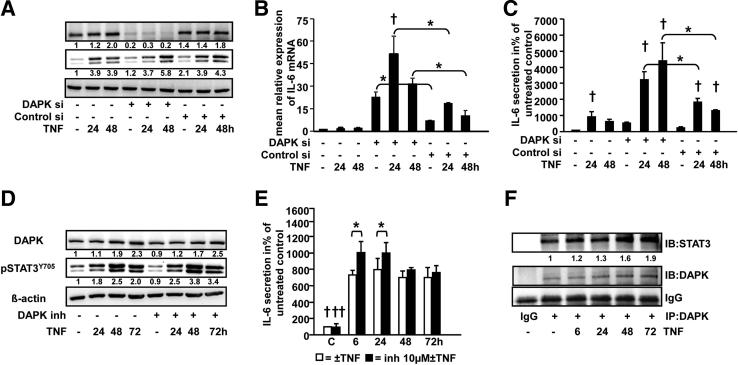
Figure 5.
DAPK attenuates TNF-induced IL-6 secretion and STAT3Y705 phosphorylation in HCEC cells. A–C: HCEC cells were treated with 0.66 ng/mL TNF for 24 and 48 hours in the presence (DAPK- or nonspecific siRNA) or absence of siRNA. A: DAPK knockdown and STAT3Y705 phosphorylation was assessed by Western blotting of whole cell lysates. B: IL-6 mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time reverse transcription-PCR. Two similar experiments were performed. *P < 0.05; †P < 0.05 versus respective control. C: IL-6 was measured in cell culture supernatants by using an ELISA. Three similar experiments were performed in duplicate or quadruplicate. *P < 0.001; †P < 0.05 versus respective control. D and E: HCEC cells were treated with 0.66 ng/mL TNF for 6, 24, 48, or 72 hours in the presence or absence of 10 μm DAPK inhibitor. DAPK and pSTAT3Y705 expression was analyzed by Western blotting (D). IL-6 was measured in cell culture supernatants by using an ELISA (E). Two independent experiments were measured in triplicate. *P < 0.05; †P < 0.001, ††P < 0.001 versus TNF ± DAPK inhibitor treatment. F: TNF-induced DAPK/STAT3 complex formation in normal human colon epithelial cells. HCEC cells were treated with 0.66 ng/mL TNF for 6, 24, 48, or 72 hours. DAPK was immunoprecipitated and complexes were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were probed with anti-STAT3 and anti-DAPK antibodies. Blots from a representative experiment (n = 2) are shown.