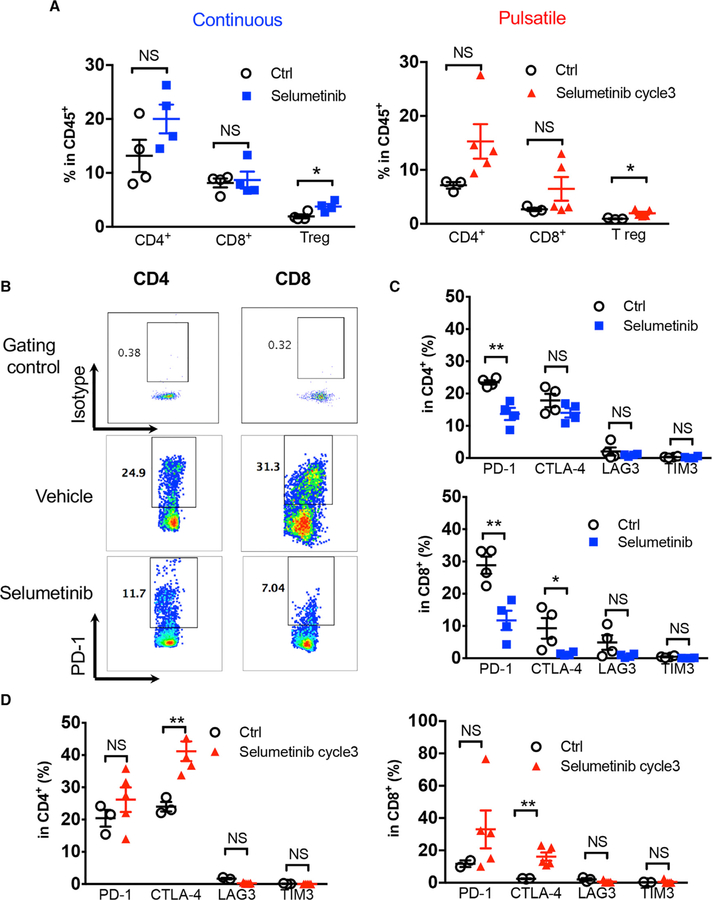
Figure 6. Co-inhibitory Signaling Was Altered Differentially by Continuous versus Pulsatile Treatment of MEKis.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of KRASG12C mutant GEMM lung-tumor-infiltrating T cell subpopulations: CD4+, CD8+, and Tregs (CD4+Foxp3+) after continuous (left) or pulsatile (right) treatment with selumetinib as presented in Figure 5A. Lung tumors were collected at the end of treatment. *p < 0.05. NS, not significant.
(B) Representative flow cytometry analysis of PD-1 levels in both CD4+ and CD8+ tumor-infiltrating T cells after continuous treatment of selumetinib.
(C) Quantification of inhibitory immune checkpoint molecule expression on CD4+ (upper) and CD8+ (lower) T cells after 3 weeks of continuous selumetinib treatment. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
(D) Quantification of inhibitory molecules within CD4+ (left) and CD8+ (right) T lymphocyte subpopulations after 3 cycles of pulsatile selumetinib treatment. **p < 0.01.
Samples were biological replicates. All mice were recruited at the same time for the treatment, and results from all mice are shown here.