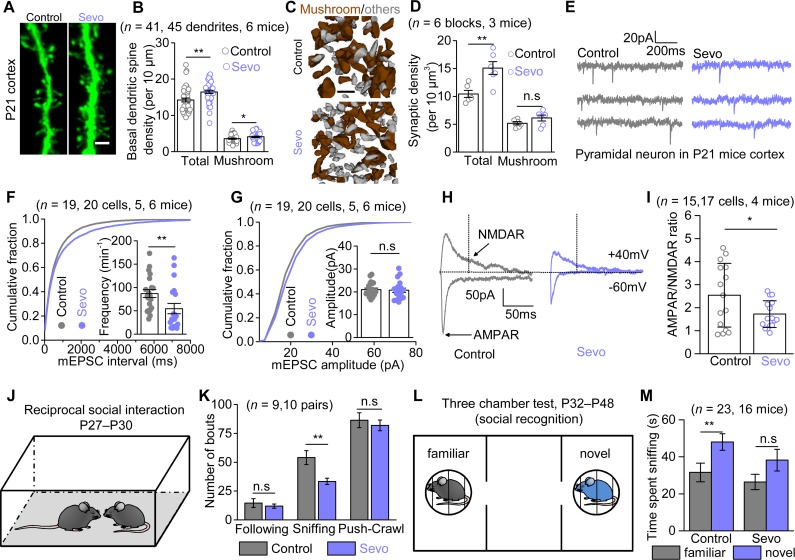
Fig 2. Aberrant synaptic growth and function along with disrupted social interactions in Sevo group mice.
(A) Representative images of basal dendritic spines in the somatosensory cortex of Control and Sevo groups at P21. Scale bar, 2 μm. (B) Quantification of the total (P < 0.001, unpaired t test) and mushroom (P = 0.039, unpaired t test) dendritic spine density in Control and Sevo groups at P21. (C) Three-dimensional reconstruction of mushroom spines (brown) and other morphologically immature spines (gray). Scale bar, 1 μm. (D) Quantification of total (P = 0.005, unpaired t test) and mushroom (P = 0.155, unpaired t test) synaptic density in mice of Control and Sevo groups. (E) Representative mEPSCs traces from L3-5 pyramidal neurons in the somatosensory cortex. (F) Cumulative distributions and average frequency (P = 0.007, Mann-Whitney test) of mEPSCs. (G) Cumulative distributions and average (P = 0.833, unpaired t test) of mEPSCs amplitude. (H) Representative eEPSCs traces from L3-5 pyramidal neurons from Control and Sevo mice at P21. The black dotted line (50 ms after the stimulation) indicated the measuring points for NMDAR-eEPSCs amplitudes. (I) Quantification of AMPAR/NMDAR ratio (P = 0.033, unpaired t test) from Control and Sevo groups. (J) Cartoon illustration for reciprocal social interaction test. (K) Quantification of the reciprocal social interaction test (following: P = 0.039, Mann-Whitney test; sniffing: P = 0.005; push-crawl: P = 0.578; unpaired t test) in pairing mice from Control and Sevo group. (L) Cartoon illustration for three-chamber test (social recognition). (M) Quantification of the social recognition test in mice of Control and Sevo groups (Control: P = 0.008; Sevo: P = 0.086; Mann-Whitney test). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n.s, not significant. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Underlying data are available in S1 Data. AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor; eEPSC, evoked excitatory postsynaptic current; L3-5, layer 3–5; mEPSC, miniature excitatory postsynaptic current; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor; n.s, not significant.