Fig. 3.
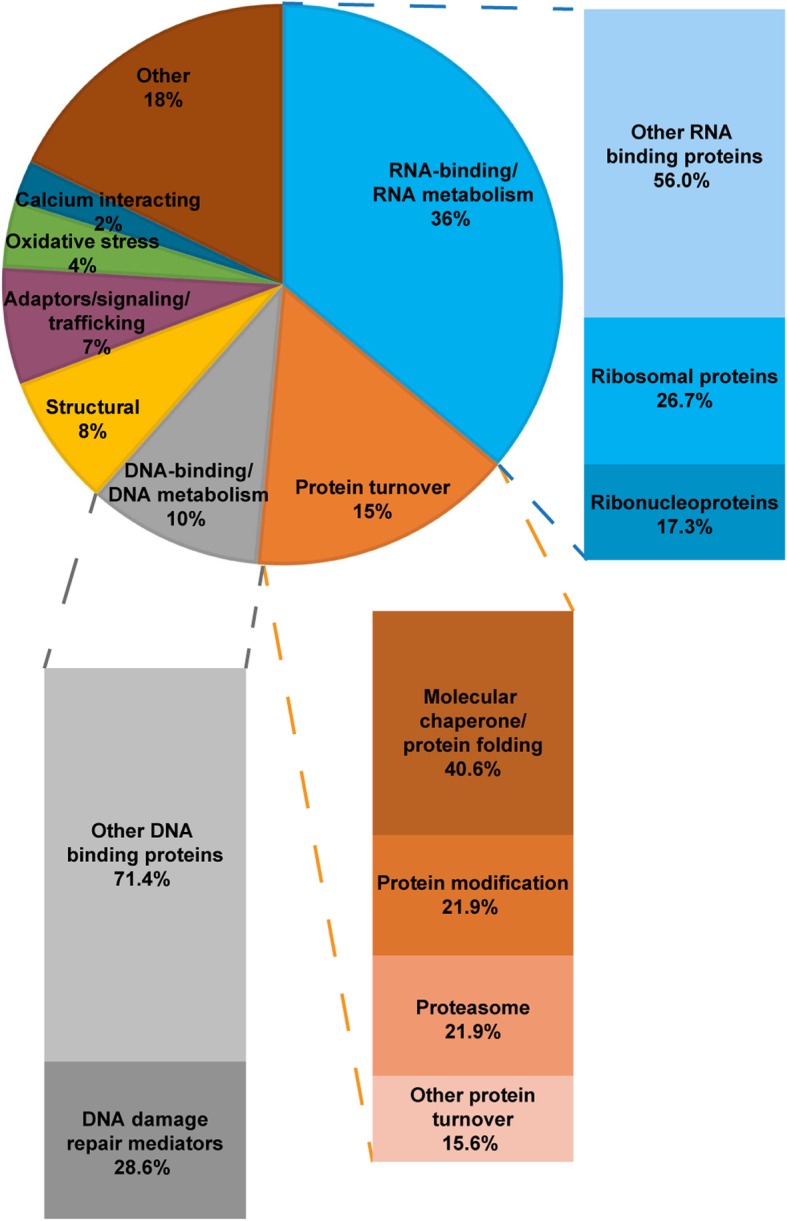
Categorization by function of inclusion-enriched proteins reveals large populations of proteins involved in RNA binding and protein turnover. Proteins that were found present to at least 0.01% in both FXTAS sorted inclusion samples and showed at least 50% enrichment in sorted inclusion samples over accompanying total nuclear samples were identified for categorization. A total of 176 proteins fit these criteria. Proteins were scored by main function(s) as identified by UniProt, and each protein could have multiple scores. Percentages were calculated as number of proteins with that score out of the total number of scores given in the dataset. The “Other” category contains proteins involved in functions including biosynthetic processes, energy metabolism, immunity, and neural development, with no one single category exceeding 3%. A total of 75 proteins were scored as RNA binding proteins and proteins participating in RNA metabolism (transcription, editing, splicing, transport). Many of the higher abundance proteins in this category were hnRNPs. Although there were many ribosomal proteins found in this dataset, almost all of them were found at low abundance (<0.1% of the total protein composition) and were not found to have more total nuclear enrichment in FXTAS nuclei compared to control nuclei. We hypothesize that these proteins represent mainly background through the isolation process and are present more as bystanders rather than main players in inclusion formation. A total of 32 proteins were scored as those participating in protein turnover (protein folding, aggregation, modification, degradation). Within this category, the majority of protein species are those involved in binding and processing proteins destined for recycling or removal. The protein species comprising this category have the highest abundance levels in inclusions. A total of 21 proteins were scored as DNA binding proteins or proteins participating in DNA metabolism (chromatin remodeling, replication, repair). Of these, 6 are players in DNA damage repair, including RAD50, RPA1, and XRCC6
