Fig 4.
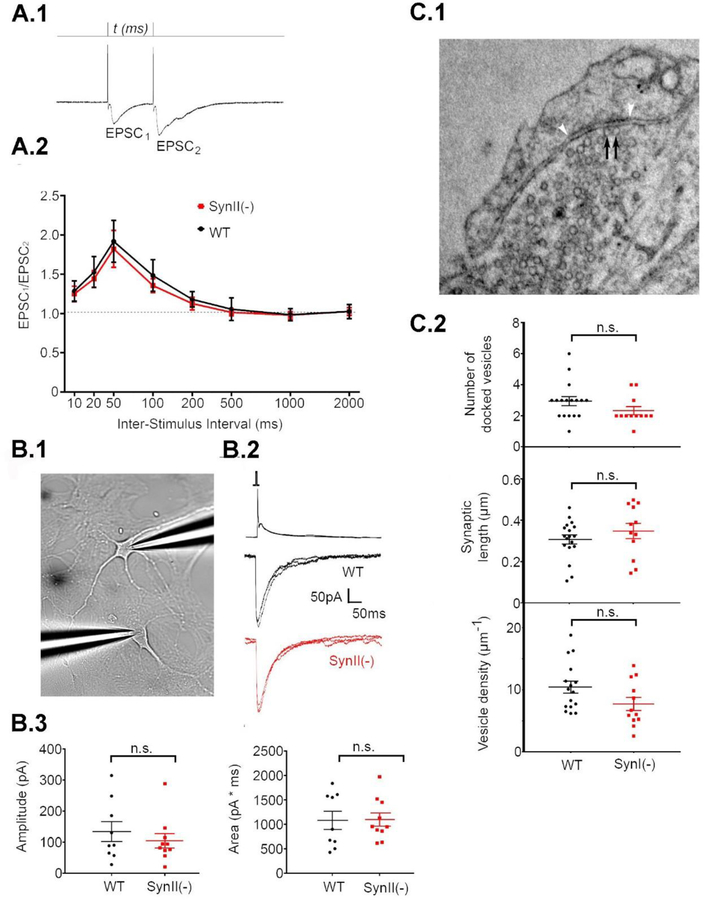
SynII deletion does not affect synaptic strength at 12 DIV. A. PPF is not affected in SynII(−) neurons. A.1. Monitoring PPF at different time intervals. The stimulation intensity was adjusted to eliminate transmission failures for the first response, EPSC1. A.2. PPF expressed at a ratio between EPSC2 and EPSC1 amplitudes. Data collected from n=9 cells (3 cultures) for each genotype. B. Synaptic currents obtained by double patch recordings from connected pairs of neurons are unaffected in SynII(−) pairs. B.1. The recoding configuration. Presynaptic action potential (top traces) coupled with EPSCs (bottom traces). B.3. Neither amplitude (left panel) or area (right panel) are affected in SynII(−) neurons. C. SynII deletion does not affect the number of docked vesicles. C.1. A representative micrograph showing docked vesicles (black arrows). The synaptic density is marked by white arrowheads. C.2. The parameters describing vesicle docking, including the number of docked vesicles per synapse (top), the length of the synapse (middle), and the density of docked vesicles (bottom).