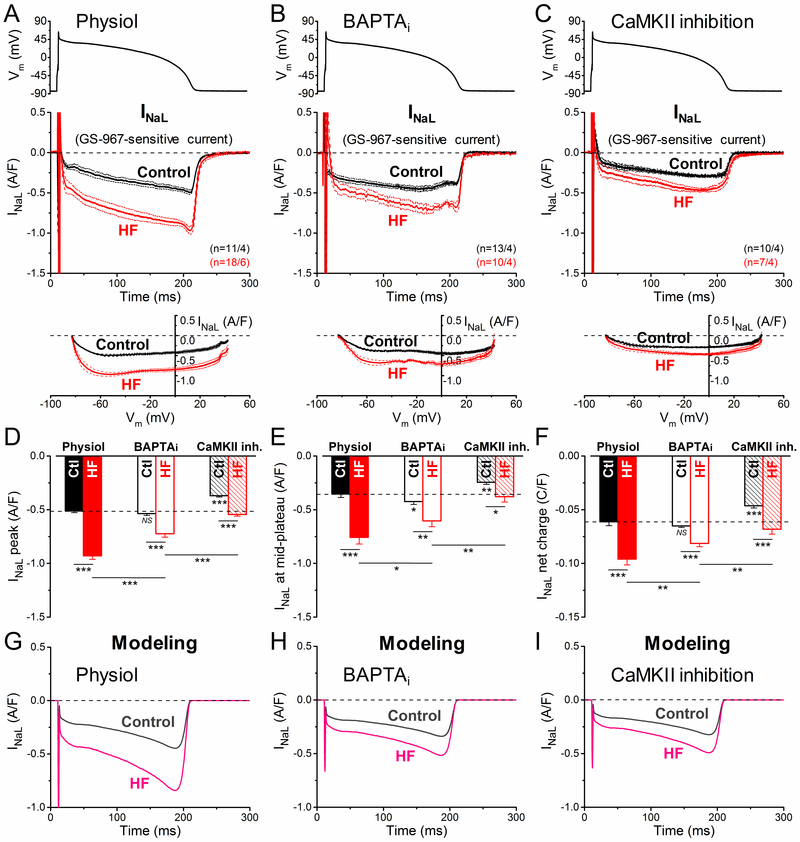
Figure 2.
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)-dependent upregulation of late Na+ current (INaL) in heart failure (HF) under action potential (AP)-clamp. INaL was measured as GS-967 (1 µM)-sensitive current in HF and age-matched control. AP-clamp using a prerecorded typical AP (shown above) was applied at 2 Hz pacing. A INaL traces (mean±SEM) recorded under preserved [Ca2+]i cycling (physiol). INaL was significantly increased already during the early plateau phase of the AP and it achieved a nearly doubled peak density during phase 3 repolarization in HF cells having Ca2+ transients. Current-voltage relationship under AP-clamp is shown below. B INaL traces (mean±SEM) recorded under buffered [Ca2+]i using 10 mmol/L BAPTA in the pipette (BAPTAi). Buffering [Ca2+]i significantly reduced INaL peak density in HF. C INaL traces (mean±SEM) recorded in cells pretreated with the specific CaMKII inhibitor AIP (autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide; 1 µmol/L). AIP reduced INaL in HF to the untreated control level; however, AIP also decreased INaL in control. D Peak INaL density was significantly upregulated in HF under AP, partially by a CaMKII-dependent acute effect on INaL. E INaL density measured at the mid-plateau of the AP. F Net charges carried by INaL under AP in HF and age-matched control. Columns and bars represent mean±SEM. n refers to cells/animals measured in each group. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni posttest, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Ctl indicates control. G-I Simulated time courses of INaL under AP-clamp in control and HF obtained with physiol, BAPTAi and CaMKII inhibition conditions.