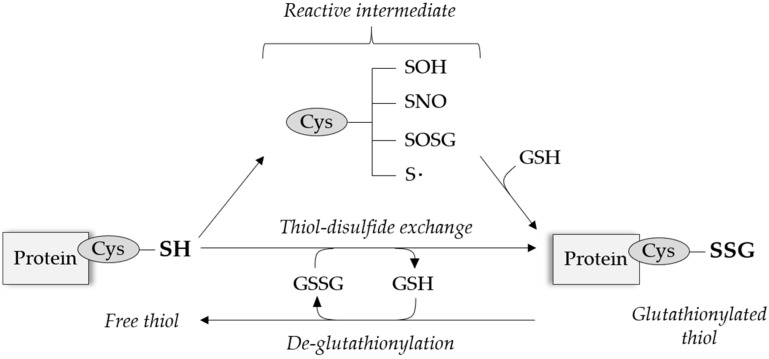
Figure 1.
General mechanisms of reversible protein S-glutathionylation. Free thiols on reactive cysteinyl residues can be modified after the formation of an intermediate thiol derivative, or more rarely undergo direct thiol-disulfide exchange. S-glutathionylation can be reversed by the action of thiol-modifying enzymes, e.g., glutaredoxin (Grx). Cys = cysteine, GSH = glutathione.