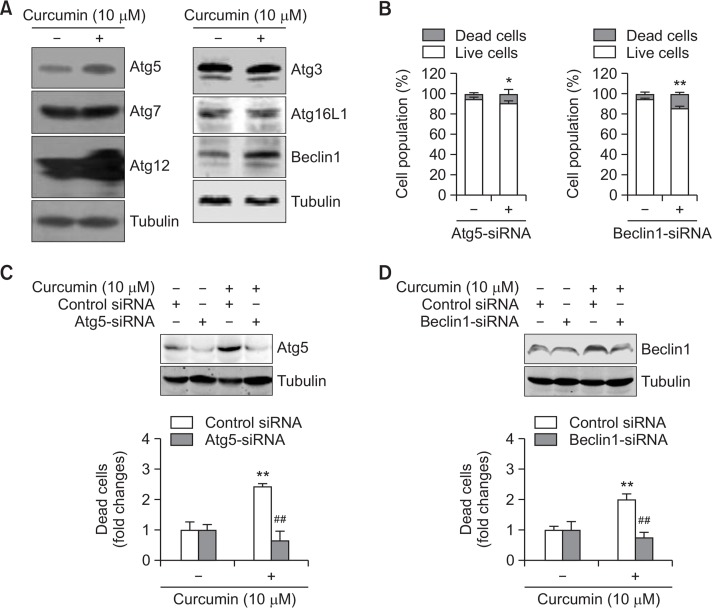
Fig. 6.
Curcumin-induced cell death was reduced by the inhibition of autophagy proteins, Atg5 and Beclin1. (A, B) A172 glioblastoma cells were treated with 10 μM curcumin for 3 (A) and 6 (B) h. Cell lysates were prepared and each autophagy protein (Atg3, Atg5, Atg7, Atg12, Atg16L1 and Beclin1) was detected by western blotting (A). Dead cells were estimated by trypan blue exclusion assay (B). (C, D) Atg5 or Beclin1 proteins in A172 cells were reduced by the transfection with Atg5-siRNA (C) or Beclin1-siRNA (D) and the incubation for 24 h. Then, cells were treated with 10 μM curcumin for 3 (top) and 6 (bottom) h. Cell lysates were prepared and LC3 proteins were detected by western blotting (top). Dead cells were estimated by trypan blue exclusion assay (bottom). Data in bar graph represent mean ±SED. *p<0.05; **p<0.01, significantly different from control siRNA-treated (B) or curcumin-untreated (C, D) group. ##p<0.01, significantly different from curcumin-treated and control siRNA-treated group (C, D).