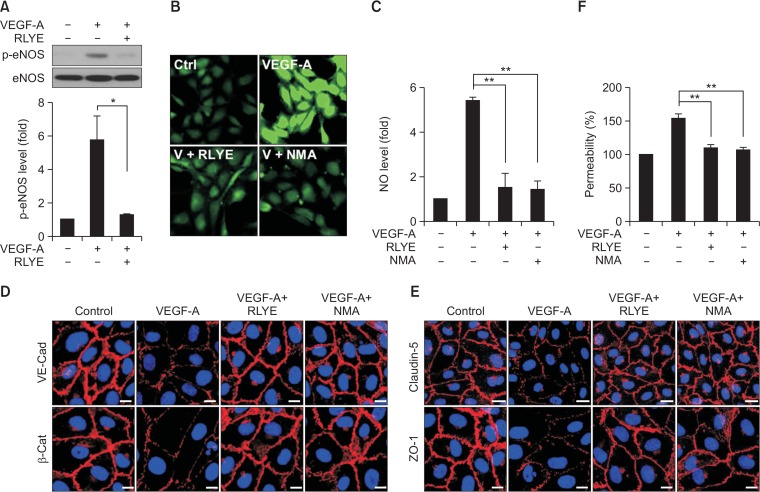
Fig. 3.
RLYE inhibits the VEGF-A-induced eNOS/NO pathway, endothelial cell junction breakage, and hyperpermeability in HRMECs. (A) HRMECs were pretreated with RLYE (0.15 nM) for 30 min and stimulated with VEGF (10 ng/mL) for 15 min. Levels of phosphorylated eNOS was determined in cell lysates by western blotting and quantified using ImageJ software (NIH) (n=3). (B, C) HRMECs were pretreated with RLYE (0.15 nM) and NMA (1 mM) for 30 min and stimulated with VEGF (10 ng/mL) for 15 min. Levels of intracellular NO production were measured by confocal microscopy using DAF-FM and quantified using ImageJ software (NIH) (n=6). (D, E) HRMECs grown in monolayers were pretreated with RLYE (0.15 nM) and NMA (1 mM) for 30 min and stimulated with VEGF (10 ng/mL) for 1 h. VE-cadherin, β-catenin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 were immunostained with their specific antibodies and secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 555. Images were obtained with a confocal microscope. Scale bar=10 μm. (F) HRMECs grown in the upper chambers of Transwell plates were pretreated with or without RLYE (0.15 nM) and NMA (1 mM) for 30 min and stimulated with 20 ng/mL of VEGF. Endothelial cell hyperpermeability was determined by measuring the amount of [14C]-sucrose that diffused through the endothelial cell monolayers (n=3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.