Figure 2.
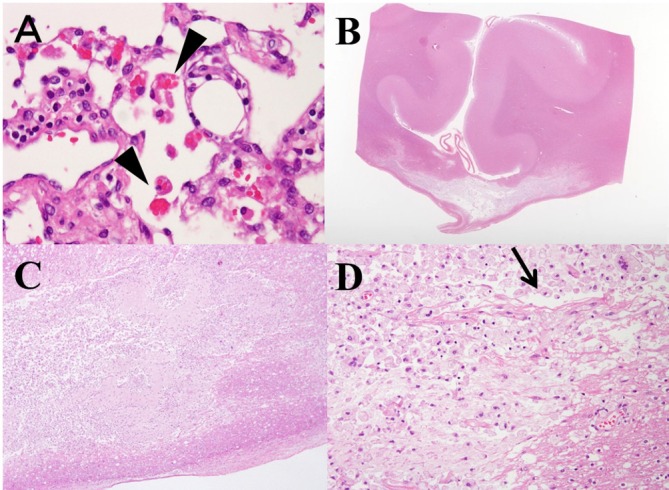
(A) Haemophagocytosis in the peripancreatic lymph node (arrow head). Haemophagocytosis is detected in the perioesophagus, peritrachial lymph node and right upper lung. (B) Histopathology of the corpus callosum (CC) through the magnifying glass revealed demyelination or necrosis in central part of the CC, while the dorsal and ventral layer was spared, which reflect characteristic ‘sandwich sign’ in MRI (H&E staining). (C) Necrotic lesions with cystic cavitations are seen (H&E staining, ×20 magnification). (D) At the central part of the lesion, most of the lesions are occupied by necrotic tissues with accumulated macrophages. There are no other inflammatory cells, like lymphocytes. Arrow head indicates cystic cavitation, which is sometimes identified with MBD patients. Myelin vacuolation seen at the lower right side suggests demyelination and few axons remains. (H&E staining, ×200 magnification). The lesions do not include old and new mixed and onset of the disease was suggested to be around the same time.
