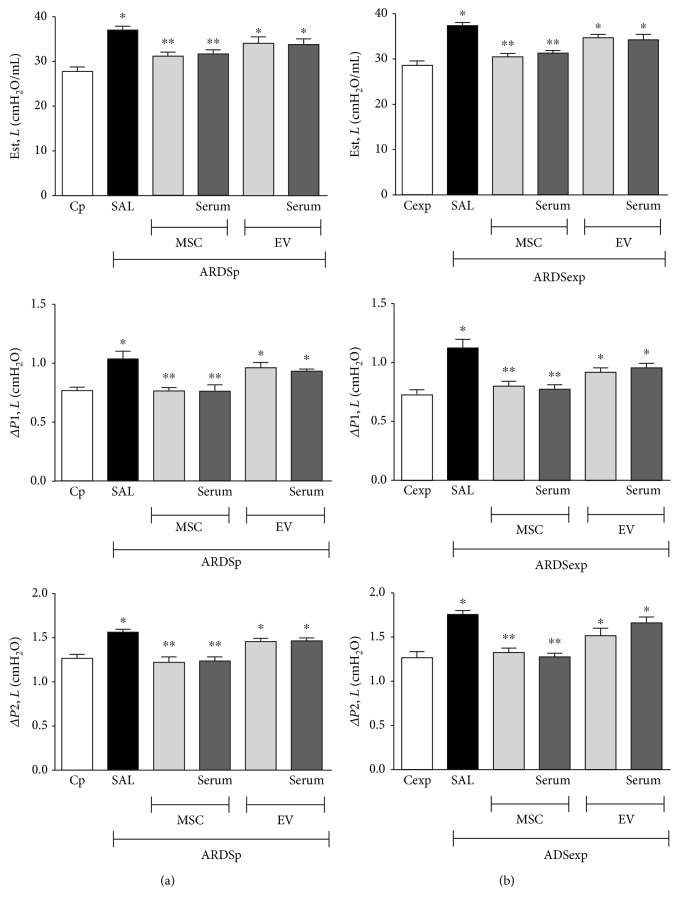
Figure 4.
Lung mechanics. Static lung elastance (Est, L) and resistive (ΔP1, L) and viscoelastic (ΔP2, L) pressures in animals with experimental pulmonary ARDS (ARDSp) (a) and extrapulmonary ARDS (ARDSexp) (b). ARDS was induced by administration of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide intratracheally (ARDSp) or intraperitoneally (ARDSexp). Control mice (C) received saline solution intratracheally (Cp) or intraperitoneally (Cexp). After 24 h, ARDSp and ARDSexp animals were further randomized to receive saline (50 μL, SAL), bone marrow-derived MSCs (105, 50 μL), or EVs (105, 50 μL), stimulated (MSC serum, EV serum) or not (MSCs, EVs) with serum obtained from ARDSp or ARDSexp animals. Values were expressed as mean + standard deviation of 6 animals per group. ∗Significantly different from the corresponding C group (p < 0.05). ∗∗Significantly different from the corresponding ARDS group (p < 0.05).