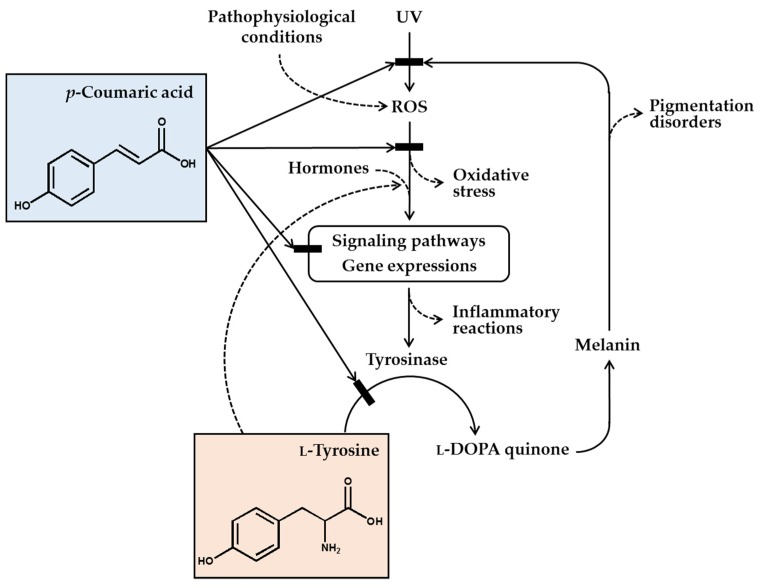
Figure 1.
p-Coumaric acid can attenuate skin hyperpigmentation through multiple mechanisms. UV and other pathophysiological conditions stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and multiple signaling pathways leading to enhanced gene expression of tyrosinase and increased melanin synthesis. The melanin can absorb ultraviolet (UV) radiation and alleviate oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions caused by UV radiation, but the melanin deposition may cause skin pigmentation disorders. p-Coumaric acid has a chemical structure similar to L-tyrosine and inhibits the activity of tyrosinase, which catalyzes the oxidation of L-tyrosine and/or L-DOPA to L-DOPA quinone in the melanin biosynthetic pathway. Due to its UV absorption and antioxidant action, p-coumaric acid can inhibit the signaling pathways linked to gene expression of tyrosinase and inflammatory mediators. p-Coumaric acid can also reduce the stimulatory effects of hormones and L-tyrosine on the gene expression of tyrosinase. Thus, it is proposed that p-coumaric acid has advantageous biochemical properties suitable for use as a skin-lightening active ingredient in cosmetics.