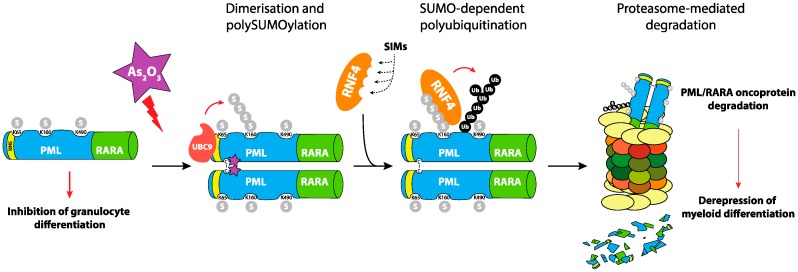
Figure 2.
Role of SUMOylation in PML-RARα degradation in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemias (APL). The oncogenic PML-RARα is responsible for the blockage of differentiation of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemic cells. Their treatment with arsenic trioxide leads to the polymerization of the fusion protein via direct binding and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent formation of disulfide bonds. This triggers its poly-SUMOylation and the recruitment of the RNF4 SUMO-targeted Ubiquitin-ligase (StUbL), which ubiquitylates PML-RARα and targets it for proteasomal degradation. This allows the reactivation of the RARα differentiation program, the reformation of PML nuclear bodies (NBs) and the induction of apoptosis of the leukemic cell.