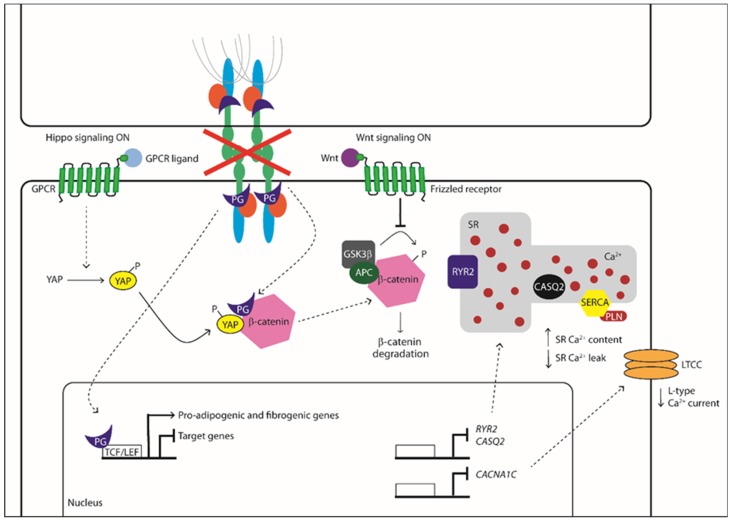
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms associated with ACM pathogenesis. GPCR: G protein-coupled receptors, YAP: yes-associated protein, PG: Plakoglobin, TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor, Wnt: homologous wingless, APC: adenomatous polyposis coli, RYR2: type 2 ryanodine receptor, CASQ2: calsequestrin 2, CACNA1C: calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 C, SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum, SERCA: sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, PLN: phospholamban, LTCC: L-type calcium channel. ( Activation/Phosphorylation,
Activation/Phosphorylation,  Translocation,
Translocation,  Inhibition).
Inhibition).