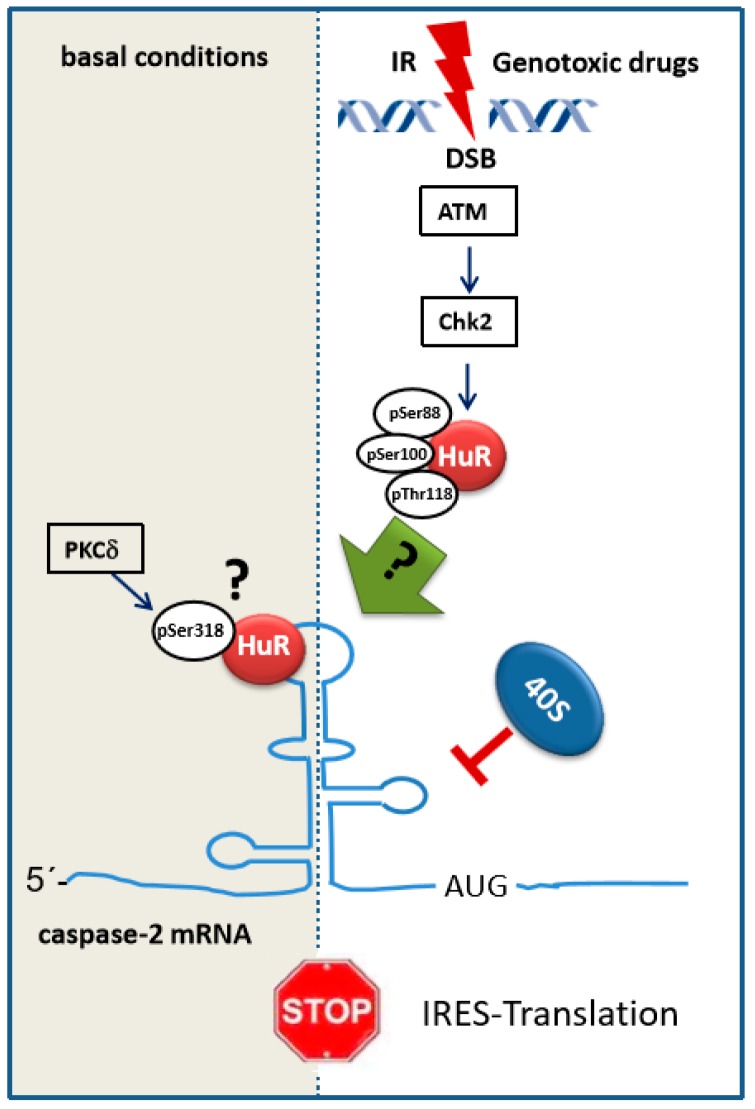
Figure 1.
Schematic model of human antigen R (HuR) mediated inhibition of caspase-2 translation and its modulation by different kinase-triggered phosphorylation events. (white panel): DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) provoked by irradiation (IR) or genotoxic drugs via the activation of a canonical ATM-Chk2 axis can induce phosphorylation of HuR, and thereby may increase its binding affintiy to the IRES of caspase-2 mRNA (indicated by a green arrow). The depicted amino acid positions represent currently known Chk2-triggered HuR phosphorylation sites which are critical for the HuR-mRNA binding. In addition, the latent HuR binding to 5´UTR of caspase-2 mRNA which is observed in human colon carcinoma cells is presumably triggered by the constitutive HuR phosphorylation by PKCδ (grey panel). The question marks indicate that the final impact of different HuR phosphorylation events for IRES binding is currently not known. HuR may act as a negative ITAF which suppresses IRES-mediated translation of caspase-2 by preventing the recruitment of the 40S ribosomal subunit to caspase-2 mRNA. Activation of the DDR may further enhance the constitutive repression of caspase-2 translation as part of a so far unrecognized cell survival mechanism. Abbreviations: ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; DSB, double-strand breaks; Chk2, checkpoint kinase 2; IR, irradiation; IRES, internal ribosomal entry site; PKC, protein kinase C.