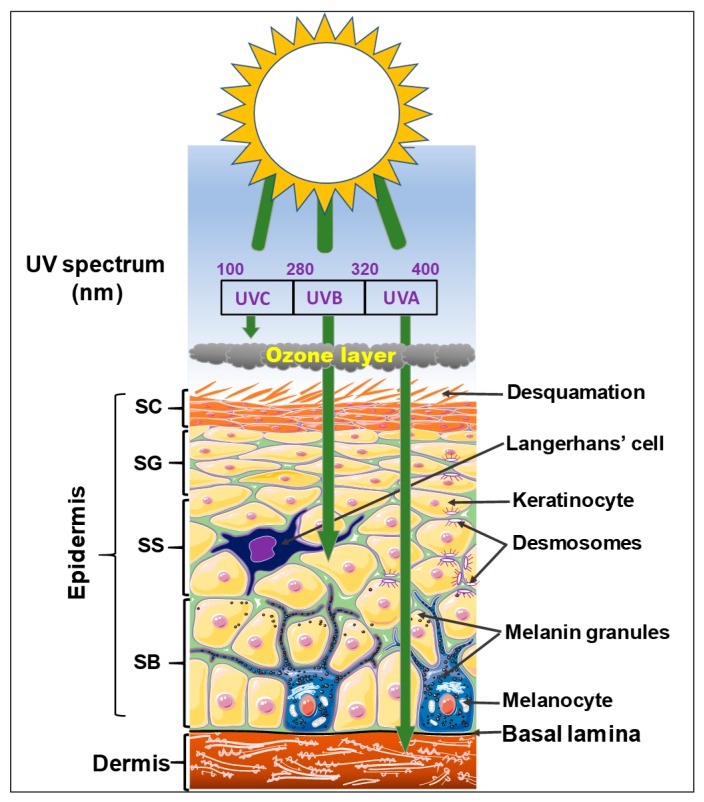
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the structure of the epidermis and papillary dermis. This stratified epithelium consists of basal, spinous, granular, lucidum, and stratum corneum layers. The basal layer contains the stem cells that sit or attach to the basal lamina via hemidesmosomes. In normal epidermis, basal keratinocytes express K5, K14, and integrins. The suprabasal and differentiating layers of keratinocytes are committed to differentiation, expressing K1, K10, and other markers, like filaggrin and loricrin. Other resident epidermal cell types include Melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. The ultraviolet rays (UVR) from the sun penetrate the atmosphere and the different layers of the skin. UVC with the greatest energy photons (shorter wavelengths) is totally absorbed by the ozone layer while UVB with intermediate energy photons (wavelengths) that damage DNA in epidermal cells penetrates the upper layers of the epidermis. UVA with low energy photons (longer wavelengths) penetrates deeper into the upper dermis causing damage to collagen and elastic tissue, even skin cancers and other skin manifestations.