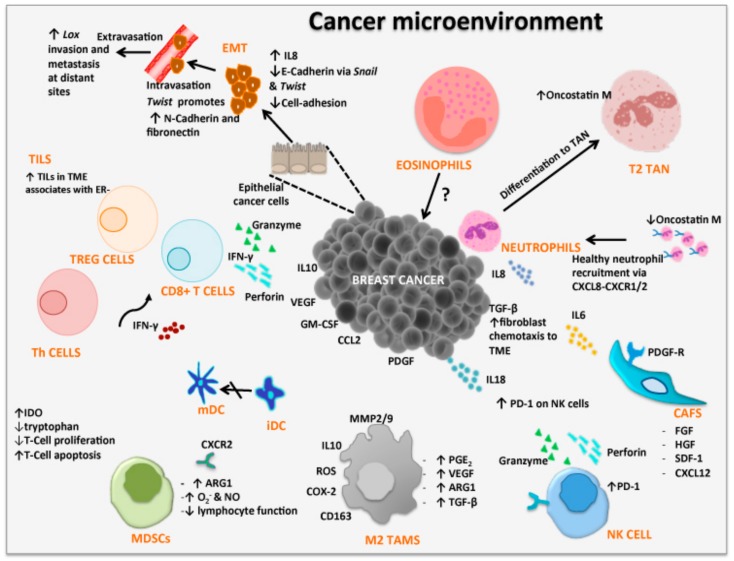
Figure 1.
Tumor-associated immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of breast cancer models. Within the TME there is an array of resident cells contributing to the progression and metastasis of breast cancer cells. The different residents and their associated secretory elements including stimulatory growth factors, chemokines and cytokines are shown. The expression of these residents within the TME of breast cancer patients may aid in discovering new markers associated with specific subtype leading to earlier diagnosis and better clinical outcome. [ARG1. Arginase 1; CAF. Cancer-associated Fibroblast; CD163. Macrophage scavenger receptor; CCL2; Chemokine Ligand 2; CXCL8-CXCR1/2. Chemokine Ligand 8-Chemokine Receptor 1 & 2; CXCL12. Chemokine Ligand 12; COX-2. cyclooxygenase-2; EMT. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition; ER− Estrogen Receptor Negative; FGF. Fibroblast Growth Factor; GM-CSF. Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor; HGF. Hepatocyte Growth Factor; IDO. Idoleamine-2, 3-Dioxygenase; IL. Interleukin; iDC. immature Dendritic Cells; mDC. mature Dendritic Cells; MDSCs. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; M2 TAMS. M2 subtype Tumor-associated Macrophage; NK CELL. Natural Killer; N2 TAN. N2 Subtype Tumor-associated Neutrophil; PDGF-R. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor; PD-1. Programmed cell death protein 1; PGE2. Prostaglandin E2; ROS. Reactive Oxygen Species; SDF-1. Stromal cell-derived factor-1; TGF-β. Transforming Growth Factor-beta; Th Cells. T-helper cells; TILs. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes; TREG. T-regulatory cells; VEGF. Vascular endothelial growth factor].